广州市近海沉积物重金属含量测定与评价研究

打开文本图片集
关键词:沉积物;重金属;含量测定;风险评价;市近海
中图分类号:X824 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1008-9500(2025)12-0184-03
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2025.12.055
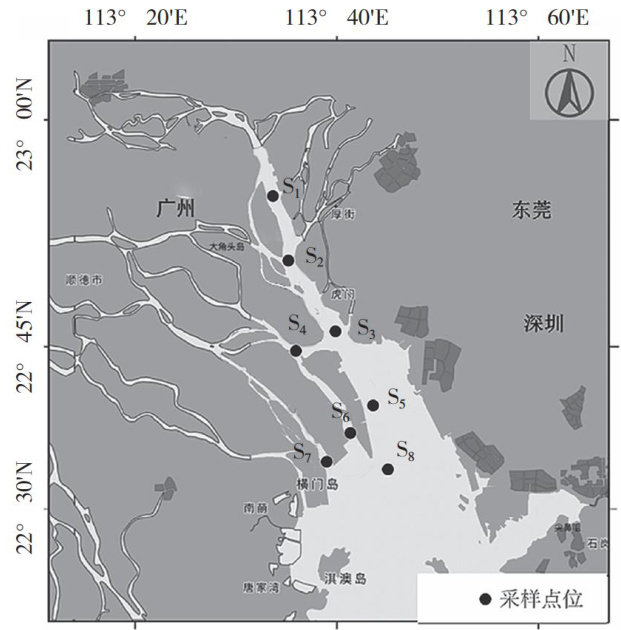
Abstract:Marinesediments mainlycome fromriver,wind,and glacier inputsof terestrial erosionmaterials,which can reflectlong-term changes in the marineenvironment.In August 2O24,8monitoring points were setupfrom theoffshore of Guangzhou city to collct surface sediment samplesand measure the contentof7 heavy metals in the sediment,the polutionstatus was studied and the geological accumulation index was usedforrisk evaluation.Theresults show that the average contentsofcopper,lead,cadmium,chromum,zinc,mercury,andasenic inthesedimentare2.8,16.6,0.4,31.7, 33.9, 0.076, and 11.5mg/kg ,respectively. The content of copper,lead, zinc,chromium,mercury,and arsenic meets the ClassI standard requirements of Marine Sediment Quality (GB18668—2002),while the cadmiumcontent at some survey sites exceeds the ClassI standard requirements of Marine Sediment Quality (GB18668—2002),but mets the ClassⅡI standard requirements.Accordingtotheeologicalaccumulationindexassssmentresults,there isnopollutionriskforlead, chromium,and zincinthe sediments fromtheofshoreof Guangzhou city,some pointshavemild polutionrisks forcopper andarsenic,mildormoderatepolutionrisksformercury,and moderatepollutionrisks forcadmium.Theorderof pollution levels of the seven heavy metals is: cadmium > mercury > arsenic > copper > lead > chromium > zinc.
Keywords: sediment; heavy metals; content determination; risk evaluation; ofshore of Guangzhou city
自然环境中,重金属具有稳定性和不可降解性,易通过食物链富集并被生物放大,最终威胁人体健康[。(剩余2808字)