基于LEAP模型的四川省交通运输碳达峰路径研究

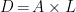
打开文本图片集
关键词:交通运输;长期能源替代规划(LEAP);情景分析;能源消费;碳达峰
中图分类号:X73 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1008-9500(2025)12-0048-06DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2025.12.015
Abstract:To address global climate change and actively participate in environmental protection,China has proposed the“dualcarbon”strategicgoal,whichhaspointedoutthedirectionforthelow-carbontransformationofthe transportation industry.Using 2O22 asthe base year,the Long-range Energy Alternatives Planning (LEAP)model is used to study the carbon peak path of transportation in Sichuan province,and four diferentiated scenarios aresetup,namely the baseline scenario,structuraloptimizationscenario,technologicaloptimization scenario,ndlow-carboncomprehensivedevelopment scenario.The energy consumption and carbon dioxide emissions of transportation in Sichuan province are predicted from 2023 to 2O40 under diferent scenarios.Based on the modelcalculation results,the carbon emissions,carbon emission structure,andemisionreduction potentialof transportationin Sichuan province areanalyzedunderdiferent development scenarios.Based on the scenarioanalysis and model calculation results,suggestions and pathways for Sichuan province's transportation carbon peak are proposed.Research has shown that in the low-carbon comprehensive development scenario and structuraloptimizationscenario,Sichuan province's transportation canachievecarbon peak,especially inthelowcarbon comprehensive development scenario where significant results are achieved.Inthe low-carbon comprehensive development senario,teenergy consumptionand carbon emisionsof transportation willreach theirpeak in2O30,witha peak energy consumptionof 38 million tons of standard coal and a peak carbon dioxide emissions of68.3 million tons.
KeyWords: transpotation;LongrangeEnergyAltemativesPlanng(LEAP);scenarioanalysis; energyconsumption;carbonpeak
全球变暖引发的一系列连锁反应对地球生态系统和人类社会造成了广泛而深远的负面影响。(剩余7803字)