基于有限元分析在接骨螺钉扭断测试中的应用

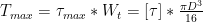
打开文本图片集
Application of Finite Element Analysis in the Torque Fracture Testing of Bone Screws
FAN Sijie
(Shanghai Institute of Medical Device Testing)
Abstract: Objective: The paper aims todesign a fixture for testing the torsional fracture torque of metal bone screws with adiametergreaterthan or equal to 5mm ,and reduce the occurrence of slippage between the screwsand the fixture before the screwsfracture,therebyimproving the success rateofthe tests.Method:According to material mechanics formulas, it analyzesthereasons whythe fracture torque ofbone screws cannot be measured due to slippage phenomena.The finite elementnalysisisusedtostablshamodel,assignmaterialproperties,onductmeshgeneration,seaalysisstesand definecontactconstraintconditions,boundaryconditions,andloads.houghfniteelementanalysis,itanalyzestheuied clamping force (reaction force)when usinga thre-jaw chuck andafixture with edges athe same embedding depth to hold the screws,andconductscomparative tests onthe successrates oftwo clamping methods.Result: The finite element analysis shows that the fixture with edges is more labor-saving when holding screws,saving nearly halfof the clamping force.The successrateoftestsusingthethre-jawchuckislowerthanthatoftestsusingthefixture withedges tohold thescrews for torsionalfracture tests.Conclusion:Usingafixture withedges tohold screws fortorsional fracture testscanimprove the success rate of the tests.
Keywords: bone screws; finite element analysis; torsional fracture torque
图6嵌入螺钉后径向投影面积
综上,具有棱边的工装夹具夹持时所需的加持力更小,应更容易的嵌入螺钉中,相同的夹持力嵌入螺纹的深度更深,切向的面积A径更大,螺纹被夹持部分可承受的最大切向力F切向max越大,螺纹越不容易被破坏发生打滑现象。(剩余2943字)