2023—2024年北京市某区生活饮用水监测分析报告

打开文本图片集
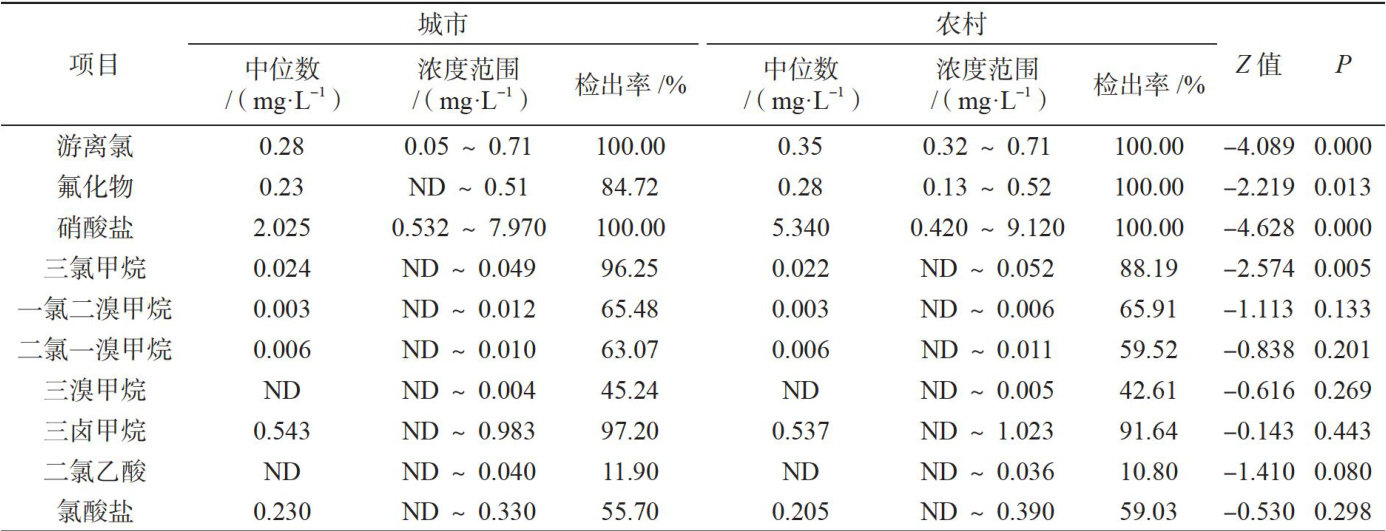
Abstract: Objective: To analyze the sanitary status of drinking water in a district of provide scientific evidence technical support decision-making by relevant authorities.Method: From 2023 to 2024,36 monitoring sites were established across l8 subdistricts (towns) in the district.Tap water samples were collcted monthly. Median values were used statistical description, non-parametric rank sum tests were applied to compare diferences between sample types water seasons.Result: Only one exceeded the stard trihalomethanes,while allother indicators met requirements.Urban tap water exhibited significantly higher trichloromethane levels than rural tap water (P<0.05 ).Conversely, eight indicators, including free chlorine, fluoride,nitrate,pH value,chloride,sulfate,total dissolved solids, total hardness were significantlylower in urban tap water compared to rural samples ( P<0.05 ). Among the nine indicators showing urban-rural disparities, six (excluding freechlorine,total dissolved solids, total hardness)demonstrated significantseasonal differences between wet dry periods (P<0.05 ). Conclusion: The overall drinking water quality in the studied district from 2023 to 2024 was satisfactory,with urban water quality outperming rural areas.Systemic upgrades are urgently needed rural water supplies, including raw water sources, infrastructure, treatment processes.
Keywords: rural domestic drinking water; chlorom; nitrate; monitoring analysis
《生活饮用水卫生标准》(GB5749—2022)对生活饮用水水质、生活饮用水水源水质、集中式供水单位卫生以及二次供水卫生均提出了要求[。(剩余2598字)