基于熵权TOPSIS法的哈尔滨市市售蔬菜农药残留状况及膳食暴露综合风险评估

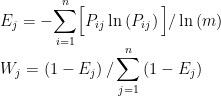
打开文本图片集
Abstract: In order to understand the status of pesticide residues in vegetables in Harbin city, this paper selects the monitoring data of vegetables from 2020 to 2024 for statistical analysis, assesses their dietary exposure, and comprehensively considers five indicators including the qualified rate, detection rate, over-limit rate, chronic intake risk and acute intake risk of various types of pesticides in vegetables. Conduct a comprehensive evaluation of entropy weight TOPSIS to assess the degree of harm caused by different types of pesticide residues. The results showed that residues of 34 kinds of pesticides such as 3-hydroxykebuvir and abamectin were detected in vegetables, and the top 5 pesticides in terms of detection rate were thiamethoxam (17.93%) , imidacloprid (15.79%) , cyf luthrin (14.75%) , thiamethoxam (13.79%) and acetamiprid (13.10%) in sequence. There were excessive phenomena of 13 kinds of pesticides in vegetables. The top 5 pesticides in terms of excessive rate were thiamethoxam (4.83%) , dipyrifos (4.00%) , abamectin (3.51%) , dipyrifos (1.75%) , chlorpyrifos (1.32%) and phenicylamine (1.32%) in sequence. Among the detected pesticide residues, oxidized dimethoate poses a chronic dietary intake risk, while triazole phosphorus poses an acute dietary intake risk. The comprehensive evaluation results of TOPSIS show that pesticide residues such as clothianidin, fenazepam, abamectin, cyf luthrin and f lamethoxam have a significant impact on human health.
Keywords: food safety risk assessment; entropy weight TOPSIS model; pesticide residue; dietary exposure
随着蔬菜种植业的快速发展,农药在蔬菜种植环节病虫害的综合防治过程中扮演着重要角色,但是它在给人们带来利益的同时,也对人体健康构成潜在威胁[1]。(剩余6394字)