油茶抗菌及抗氧化活性研究

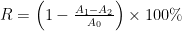
打开文本图片集
Abstract: Objective: To systematically evaluate the antibacterial activity of Camellia oleifera against three common pathogenic bacteria (Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus epidermidis and Bacillus subtilis)and itsability to scavenge DPPH free radicals,providing a scientific basis for the natural preservation and antioxidant applications of Camella oleifera.Method: The inhibition zone diameter was measured using the paper disc diffsion method, the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) was determined using the serial dilution method,and the antioxidant capacity of Camelia oleifera was quantitatively analyzed through the DPPH free radical scavenging assy combined with avitamin Cstandard curve.Result: Cameliaoleifera exhibited the strongest inhibitory efecton Staphylococcus epidermidis,with an inhibition zone diameter of (12.67±0.65) mm, followed byBacillus subtilis[ (10.33±0.58) mm] andEscherichiacoli[ (7.33±0.25) mm],showing a concentration-dependent antibacterial activity.The DPPH free radical scavenging rate of Camelia oleifera was also concentration-dependent. When the mass concentration of Camellia oleifera was 80mg⋅mL-1 ,the scavenging rate reached 81.49% ,which was comparable to the antioxidant effect of vitamin C.Conclusion: Camella oleifera possesses both broad-spectrum antibacterial activity and strong antioxidant capacity.Its mechanisms maybe related to its rich content ofactive ingredients suchas polyphenols and vitaminE,making it a promising candidate for development as a natural food preservative or functional additive.
Keywords:Camelliaoleifera;antibacterial;DPPH freeradical;antioxidant
油茶是富含不饱和脂肪酸、茶多酚、角鲨烯等活性成分的天然植物油,具有抗氧化、抗炎和调节血脂等潜在药理作用[1-2]。(剩余3792字)