观察无创呼吸机治疗阻塞性睡眠呼吸 暂停低通气综合征疗效

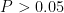
打开文本图片集
AbstractObjective:Toexploretheclinicaleficacyof non-invasiveventilators inthetreatmentofobstructivesleepapnea-hypopnea sydrome(OSAHS).Methods:Atotal of119 patients diagnosed with OSAHSandtreatedatYuxi People's Hospital from January 2021 to April2O25were selectedas the study subjects.They were randomlydivided intoa control group( n=74 )and an observation group( n=45 )using a random number table method. The control group received health education,exercise promotion, weightloss,andactivepreventionandtreatmentofcomplications.Theobservationgroupreceivednon-invasiveventlationtreat ment with a ventilator in addition to the control group for more than 3 months.Nocturnal minimum oxygen saturation( SaO2 ),apnea-hypopeaindex(AHI),and polysomnography(PSG)valuesof patients wererecorded beforeandafter treatmentResults:After intervention,bothgroupsofpatientsshowedadecreaseinAHIlevelsandtheobservationgroupwassignificantlylowerthanthe control group. The difference between the two groups was statistically significant ( P<0.05 ).After intervention,minimum SaO2 (20 levelsinbothgroupsofpatientsicreased,withtheobservationgroupwassignificantlyhigherthanthecontrolgroup.Tediference between the two groups was statistically significant( P<0.05 ). The total effctive rate of treatment in the observation group wassignificantlyhigherthanthatinthecontrolgroup,andthedferencebetweenthetwogroupswasstatisticallsigificant( P< 0.05).Conclusion;Forpatients with OSAHS,theuseof non-invasiveventilatorsforlong-termtreatmenthassignificantherapeutic effects.This treatment method has high clinical application valueand is worthyofclinical promotionandapplication.
KeywordsObstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome;Non-invasive ventilator;Continuous positive airway pressure ventilaon;Polysomnography;Disease grading;Effective treatment rate; Long-term treatment;Efficacy
中图分类号:R338.63;R364.4 文献标识码:A doi:10.3969/j. issn. 2095 -7130.2025.08.014
阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征(Obstructive 害严重的源头性疾病,与多种疾病关联密切,显著增Sleep Apnea Hypopnea Syndrome,OSAHS)是一种危 加了高血压、冠心病、糖尿病等多种心脑血管疾病的
发病风险[1],病情严重者甚至可能导致夜间猝死。(剩余4182字)