自我赋权联合正念减压训练对肠癌术后患者睡眠的影响
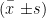
打开文本图片集
AbstractObjective:To explore theefectsof self-empowerment combinedwith mindfulnessbased stress reduction(MBSR) training onsleepinpostoperativecolorectalcancerpatients.Methods:Atotalof7OpostoperativecolorectalcancerpatientsadmittedtoTeFirstAflitedHospitalof XiamenUniversityfromMay2O23toMay2O24wereselectedasthestudysubjects.They weredividedinto acontrol groupandanobservation group(35 patients each)using arandom number table method.The control groupreceivedroutinepostoperative interventions,whiletheobservation groupreceived self-empowermentcombined with MBSR training interventions.Thepsychologcalstateself-ratingdepresionscale(SDS),self-ratigaxietyscale(SAS)],puality [Pitsburgh SleepQualityIndex(PSQI)],self-eficacyStrategiesUsedbyPeople toPromote Health(SUPPH)]andqualityof life[the World Health Organization QualityofLife-Brief Version(WHOQOL-BREF)]were observedandcompared between the two groupsafterteinterventionResults:Comparedwithontrol group,afterinterventio,theobservationgrouphadsignificantly lower PSQI scores,SDS scores,and SAS scores,with statistically significant differences ( P<0.05 ). The observation group also hadsignificantlyhigherscoresinalldomainsof theWHOQOL-BREFandhigherSUPPHscores,withstatisticallysignificant differences ( P<0.05 ). Conclusion:The application of self-empowerment combined with mindfulness-based stress reduction training npostoperativecolorectalcancerpatientscanimprove theirsleepqualityandaleviate negativeemotions,hilealsoenancing self-efficacy and quality of life.
KeywordsPostoperativecolorectalcancer;Self-empowerment;Midfulness-basedstressreductiontraining;Psychologicalstatus;Sleep quality ;Self-efficacy ; Quality of life
中图分类号:R473.6;R473.73 文献标识码:A doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-7130.2025.05.057
肠癌为消化道常见恶性肿瘤,发病率逐年增长,严重威胁患者生命健康[1]。(剩余6130字)