自标导向镇静策略干预对重症患者多导睡眠监测下睡眠结构影响观察
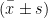
打开文本图片集
AbstractOjective:Toobservetheefectsofearlygoal-directedstrategy(EGDS)onSleparchitectureincriticallillpatints monitoredbypolysomnography(PSG).Methods:Atotalof90patientsadmited totheintensivecareunitof thehospitalwereenroledastheresearchobjectsbetweenOctober2022andOctober2024.Accordingtoandomnumber table method,theyweredivided intoobservation group(EGDS)andcontrolgroup(routinesedation),45casesineachgroup.ThesleepqualityPitsburgh SleepQuality Index(PSQI),SleeparchitectureunderPSG]andclinical indexes(durationof mechanical ventilation,staytime in ICU,extubationtime)werecompared betweenthetwogroupsbeforeandafterintervention.Results:Theclinical indexes inthe observation group were better than those in the control group( P<0.05 ). After 3 d of intervention,rapid eye movement/effective sleep % (REM % ),sleep efficiency(SE),stage N1/effective sleep % ( N1% ), stage N2/effective sleep % ( 1% )and stage N3/effective sleep % ( N3% )in observation group were better than those in control group( P<0.05 ).After3dof intervention, scoresof PSQI(slepquality,sepdisturbance,fallngasleeptime,sleeptie)intheobservationgroupwere higherthanthosein the control group( P<0.05, ). Conclusion:EGDS intervention improves sleep architecture and quality while accelerating recovery in critically ill patients.
KeywordsGoal-directed;Sedation;Criticallillpatients;Polysomnographymonitoring;Sleeparchitecture;Sleepquality
中图分类号:R459.7;R338.63 文献标识码:A doi:10.3969/j. issn. 2095 -7130.2025.05.014
重症患者在ICU中通常难以保障睡眠质量,易发生总睡眠时间减少、睡眠片段化、睡眠结构异常及昼夜节律紊乱等现象,阻碍患者的自然体力恢复与康复进程,严重者甚至可出现认知功能障碍和长期后遗症[1]。(剩余4632字)