非药物睡眠干预对重症监护成人患者谵妄和睡眠质量的影响
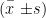
打开文本图片集
AbstractObjective:Toexploretheefectsofnon-pharmacologicalsleepinterventionondeliriumandslepqualityincriticaly illadult patients.Methods:Atotalof1OadultpatientsadmitedtotheintensivecareunitofQuanzhouFirstHospitalfromJanuary024to February 2O25 wereselectedas the studysubjects.Theywererandomlydivided intoacontrol groupandanobservationgroupusingarandomnumber tablemethod,with-55patients ineach group.Thecontrolgroupreceivedroutinesleepinterventionforcriticallyillpatientshiletheobsevationgoupreceivedon-pharmacologicalslpintervention.ThePitsburghSleep QualityIndex(PSQI)wasusedtocompare thediferences in sleepqualitybetweentwo groupsof patientsbeforeandafterintervention.Apolysomnographymonitorwasused torecordawakening frequencyandnightimeslepduration.TheConfusionAssessment Methodfor theICU(CAM-ICU)wasused toasess delirium improvement.Diffrences indelirium incidence,durationof delirium,anddaysof mechanical ventilationwere alsocompared.Results:Aftertheintervention,theobservationgroupshowedsignificantlylowerPSQIscores,significantlyfewerawakeningsandsignificantlylongernightimesleepdurationcomparedtoheontrol group,with statistically significant differences( P<0.05 ).Additionally,the observation group had significantly fewer days of delirium,fewerdaysofmechanicalventilation,andasignificantlylowerdeliiumincidenceratecomparedtothecontrolgroupith statistically significant differences ( P<0.05 ). Conclusion: Non-pharmacological sleep interventions can effectively improve sleep quality,reduceteicidenceofeliumandpromoteaceleratedrecoveryiniticallilladultpatients,akingtworyf clinical promotion and application.
KeywordsIntensivecare;Adult; Delirium;Eye mask;Earplugs;Awakening frequency;Sleepquality;Mechanical ventilation
中图分类号:R248.1;R338.63 文献标识码:A doi:10.3969/j. issn. 2095 -7130.2025.05.005
在重症监护室中,患者出现谵妄的情况较为普遍,通常表现为感知、意识和注意力的不稳定[1]。(剩余5744字)