甘肃高原驻防官兵睡眠障碍及胃肠道疾病情况调查
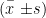
打开文本图片集
AbstractObjective:To investigatetheprevalenceof sleepdisordersandgastrointestinal diseasesamong plateau-garrioned trops in Gansu,analyzecontributingfactors,proposepreventive measures,andprovidereferencesforimproving high-altituemedicalsupportsystems.Methods:Aquestionaire-basedsurveywasconductedamong 35Ogarisoned troopsontheGansuPlateau.Dataonsleepdisorders,astrointestinaldiseases,ndbehavioral factors(smoking/teaconsumption)werestatisticallyanalyzed Results:A total of 304 valid questionnaires were collcted. Sleep disorder prevalence : 42.1% , primarily manifesting as dream-disturbed sleep(78.2%) and sleep-onset difficulties(65. 7% );Gastrointestinal disease prevalence : 39.5% ,with abdominal distension( 63.4% )and diarrhea ( 51.2% )being most frequent;Tea consumption was significantly higher in troops with sleep disorders( P<0.05 ); Smoking rates were significantly elevated in troops with gastrointestinal symptoms( P<0.05 ) . Conclusion;Altitude exposuresignificantlyimpactssleepqualityandgastrointestinal health ingarrsonedtroops.Countermeasures should prioritizeEarlypreventioofaltitudehypoxia-inducedphysiologicalresponses.Idividualizedtreatmenprotocolsforsevere cases. Systematic interventions to ensure health status and enhance combat effectiveness.
KeywordsPlateau;Garison troops;Altitude hypoxia;;Sleep disorders;Gastrointestinal symptoms;Prevalence;questioaire survey
中图分类号:R338.63;R364.4 文献标识码:A doi:10.3969/j. issn.2095 -7130.2025.05.016
睡眠障碍是指在睡眠-觉醒周期中出现的身体功能异常。(剩余4569字)