急诊胸痛留院观察患者睡眠质量影响因素调查研究

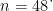
打开文本图片集
Investigation and Study on Factors Influencing Sleep Quality of Patients Underwent Observation for Emergency Chest Pain
JIANXiaohua
(Xingpu Hospital,Suzhou 215126,China)
AbstractObjective:To exploretheinfluencing factors influencing sleepqualityinpatientsunderwentobservation withchest painin emergencydepartmentMethods:Atotalof8OchestpaipatientsadmitedtotheemergencydepartmentofXingpu Hospitalin SuzhouIndustrial Park from January2023to December 2O23 wereselectedastheresearch subjects.The Pitsburgh Sleep Index(PSQI) was used to evaluate the sleep quality of patients. A PSQI score >7 was classified as poor sleep quality( n=32 ) and included in the poor sleep quality group. A PSQI score ⩽7 was classified as good sleep quality and included in the good sleep quality group( n=48 ). Using multiple logistic regression analysis to explore the influencing factors of sleep quality in emergencycestpain patients underobservation.Results:Theproportionof patientswithpoorslepqualitywhohadahistoryof coronaryheartdisease,hypertension,nightimeawakeninghabits,anddrinkingstrong teaorcoffeewas higherthanthatofthegroup withgoodsleepquality.Therevisedlifeorientationtest(LOT-R)scores werelowerthanthoseofthegroupwithgodslepquality ( P<0.05 ).The results of multiple logistic regression analysis showed that a history of coronary heart disease( OR=1.455 ),a history of hypertension( OR=1.364 ),a habit of nighttime awakening( OR=1.203 ),a habit of drinking strong tea or coffee ( OR=1 . 163),and LOT-R( OR=0.717 ) were the influencing factors on the sleep quality of emergency chest pain patients who were hospitalized for observation( P<0.05 ). Conclusion: A history of coronary heart disease,hypertension,nighttime awakening habits,consumptionofstrong teaorcofeeandLOT-Rscoresareinfluencing factorsonthesleepqualityof patientswithmergency chest pain who are hospitalized for observation.
KeywordsChestpain;Emergencytreatment;Hospitalizedforbservation;Sleepquality;Analysisofinfluencingfactors;itsburgh Sleep Index Scale;Revised version of life orientation test;Coronary heart disease
中图分类号:R338.63 文献标识码:A doi:10.3969/j. issn.2095-7130.2025.02.057
急性胸痛构成了急诊科接诊病例的 20% 至30% [1],其成因多样,可能涉及心血管疾病、呼吸系统问题,以及胸部骨骼、肌肉或神经方面的疾病。(剩余5045字)