头颅磁共振成像在类似发作性睡病脑梗死中的应用和临床价值研究

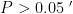
打开文本图片集
Study on Application and Clinical Value of Head Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Cerebral Infarction Similar to Narcolepsy
ZHOU Hao1,LIU Zhongkai²
( I Department of Medical Imaging,Yancheng Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Yancheng 2240o,China; 2 Department of Tuina,Yancheng Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Yancheng 240oo,China)
AbstractObjective:To identifytheresponsible vessel andlocationofcerebral infarctionwithnarcolepsybyaalyzingthe head magneticresonance imaging images,andtoprovidedetailedinformationforclinical treatment.Methods:From January 2023to December2O24,3O patientswithcerebral infarctionsimilar tonarcolepsywereselectedastheobservationgroup.Thirtyhealthy subjects wereselectedasthecontrol group.Allsbjectsunderwent magneticresonanceimagingofthehead.Results:Al30patientshad excesivedaytime sleepinessand sleepdisordersatnight.Theresultsof difusion-weighted imaging parametersof the two groupsshowed that theanisotropy index,averagedispersioncoeficientandvolumeratioanisotropyof theobservation group were lower than those of the control group,while the atenuation index was higher than that of the control group( P<0.05 ). Head magneticresonanceimagingsowedthatalltediseasedvesels involvedthalamictuberousartery.Theinfarctareas involvedthalamicreticularnucleus,anteriorthalamicnucleus,subthalamicnucleus,paraventricularoroccipitallobe,and cerebellum.Conclusion;Thediseasedvesselofcerebralinfarctionwitharcolepsyisthalamictuberousartery,theinfarctaras may involve multiple parts of thalamus,and some patients may show cognitive decline.
KeywordsCerebral infarction;Narcolepsy;Magneticresonanceimaging;Cerebrovasculardiseases;Cognitive function;Lethargy ; Sleep disorders; Thalamus
中图分类号:R338.63;R743.3 文献标识码:A doi:10.3969/j. issn. 2095 -7130.2025.02.012
发作性睡病是一种慢性睡眠障碍,其特征是睡眠-觉醒周期紊乱和快速眼动期睡眠干扰[1]。(剩余5978字)