水资源安全与粮食生产韧性耦合协调特征及驱动因素研究
——基于中国粮食主产区的实证

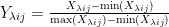
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:F32 文献标识码:A 文章编号:2095-5553(2025)07-0310-09
Abstract:The coordinateddevelopmentof waterresourcesecurityandgrain productionresilience is crucial for promoting high-qualityagricultural developmentandensuring food securityin China.Using provincial panel data from major grain-producing regions between 2004 to 2022,a comprehensive evaluation index system was established to assess both water resource security and grainproduction resilience.The entropy method,coupling coodination degree model,andgeographical detectorwereapplied to quantitativelyanalyze theevaluationvalues,coupling coordinationcharacteristics,and driving factors behind these two systems.Theresults revealeda generalimprovement in both water resource securityand grain production resilience across the major grain-producing regions.The coupling coordinationdegree between thetwo systems has steadily increased,shiftingfroma stateof near imbalance tooneof tentativecoordination.Spatially,thecoordination followedapatterndescribedas“highinthenorthandlowinthe south, withtwo clusters”.Fivekeyindicators were identifiedasprimary driversof coordinated development:effective irrigation area,annual precipitation,sewage treatmentrate,local fiscal expenditure on agriculture,forestry,and wateraffairs and total watersupply.The influenceof these factors was found to increase when they interacted with each other.Therefore,toaccelerate agricultural modernization, major grain-producing areasshould notonly improve water resourceutilization eficiencybutalsotailor development models tolocalconditions inorder topromote the integrated advancements of water security and grain production resilience. Keywords: water resource security; grain production resilience; coupling coordination; driving factors
0 引言
粮食生产对水资源的依赖程度高,我国水资源总量丰富,但单位面积耕地占有的径流量仅为世界平均值的 80% ,且时空分布极不均衡,是水资源严重短缺的国家之一。(剩余14595字)