2021一2024年历城区食品风险监测微生物污染状况分析

打开文本图片集
Analysis of Microbial Contamination Status in Food Risk Monitoring in Licheng District from 2021 to 2024
YAOZengyun,DUYuankun,CUI Yingxue,KANGYuhan,XUJingkun (Licheng District Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Jinan 250lO0, China)
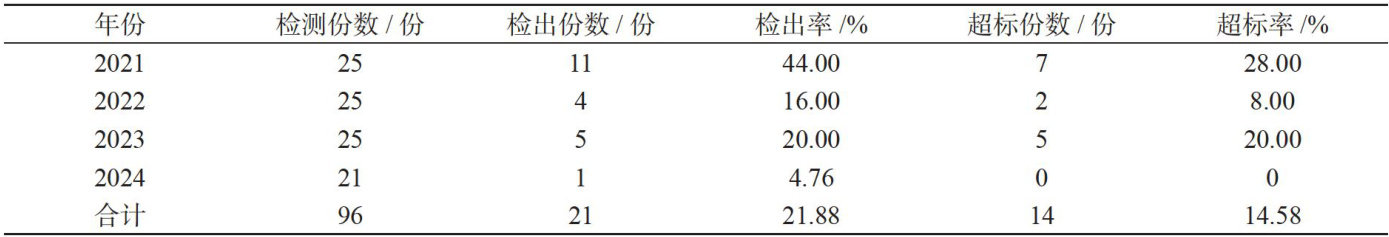
Abstract: Objective:To identify high-risk microbial contamination factors in differenttypes offood and conduct targeted monitoring,providing a basis for food safety risk assessment and early warning,and ofering scientific guidance forresidents’healthy diet.Method:From 2021 to 2024,various types of food were collected and tested forhygiene indicatorbacteria,foodborne indicator bacteria,and norovirus.Result: Atotal of96 food samples were tested from 2021 to 2024. The detection rate of microbial indicators was 21.88% , and the over-limit rate was 14.58% No foodborne pathogenic bacteria were detected.The over-limit foods and their over-limit rates were:cooked flour and rice products around schools (40.00%) ,takeout food (100.00%) ), and animal seafood (71.43% ).Theover-limit indicators and their over-limit rates were: total colony count (5.88%) ,coliform bacteria (29.03%) ,and norovirus (71.43%) .Theover-limit rate of food in supermarkets ( 0% )was lower than that in other catering links (19.05%) , farmers’markets (71.43%) , and online stores (100.00%) ). The over-limit rate of prepackaged food (0%) was lower than that of bulk food (28.57%) ). The over-limit rate of coliform bacteria in cold noodles was 100.00% , and cold noodles accounted for 66.67% of the over-limit catering foods. Conclusion: Animal seafood has a relatively high risk of norovirus contamination,and it is advisable to avoidconsuming raw or insuffciently heated seafood.Cold noodles have a high risk of coliform bacteria contamination and should be given special attention.
Keywords: food; risk monitoring; microbial contamination; foodborne pathogenic bacteria; norovirus
食品在生产加工及销售过程中有可能因各种原因而导致微生物污染,微生物污染水平会受到食品特性、加工和处理方式、储存及运输条件、环境卫生状况以及初始污染水平等因素的影响。(剩余5325字)