Sentinel-2遥感影像在天山北坡乔木林地上碳储量估算中的应用

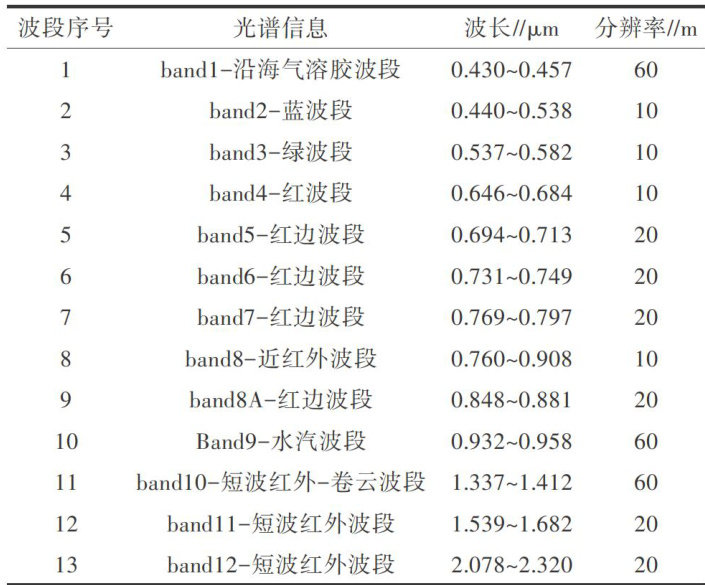
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S771.8 文献标识码:A文章编号:0439-8114(2025)06-0190-07DOI:10.14088/j.cnki.issn0439-8114.2025.06.032开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID)
Application of Sentinel-2 remote sensing imagery in aboveground carbon storage estimation ofarboreal forestsintheNorthSlopeof TianshanMountains
ZHAO Bing-jie,GAO Peng-yuan,WANG Chun-bo, ZHAO Wei-chang,ZUO Wei-kun, LIANGDai-song,SI Lei (Geophysical Survey Teamof HebeiProvinceCoalfieldGeology Bureau(Hebei Coal Underground Gasification Research Center), Xingtai 054000,Hebei,China)
Abstract:ToexplorethepotentialofSentinel-2forestimatingabovegroundcarbonstorageinarborealforestsontheNorthSlopeof TianshanMountains,apilotstudywasconductedusingSentinel-2remotesensingimageryfrom2O21andquadratsurveydata.Bntegratingspectralinformation,vegetationindices,texturalfeatures,andtopogaphicfactors,optimalvariablesweresrendusing mean residual sum of squares ( RMS ),akaike informationcriterion( .AIC ),andadjusted coefficient of determination (R2-adjust). Both thepartialleastsquaresregresionmodelandtherobustestimationmodelweredeveloped,withtheiraccuracyevaluatedthroughthe coefficient of determination (R2), root mean square error ( E⋅RMS ),relative root mean square eror( ERRMS ),and bias ( bbias ). The results showed that 22 highly significant remote sensing factors ( P<0.01 )were extracted from Sentinel-2 remote sensing imagery data,with 7 modelingfactorsultimatelyselectedthroughvariableoptimization.Thesefactorscoveredthreecategories:Spectral information (band11,band12,band4,band5),vegetationindices(NDVI,RVI),and textural features(b11-Mean).Boththepartial least squaresregresionmodelandrobustestimationmodeldemonstratedhighpredictiveaccuracyandreliability,withtheformeutper formingthelater.TheresultsindicatedthestrongpliabilityofSentinel-2forabovegroundcarbonstorageestimationinrboealfor ests on the North Slope of Tianshan Mountains.
Keywords:Sentinel-2;remotesensingimager;arborealforests;abovegroundcarbonstorage;partialleastsquaresregresino bust estimation;the North Slope of Tianshan Mountains
随着全球气候变化日益加剧,大气中二氧化碳浓度和气温不断升高,增强陆地生态系统固碳能力成为应对气候变化的重要途径[1]。(剩余8418字)