农科教育智能化转型实证探索
——融合因果推断与多元数据的路径分析

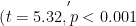
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:G640 文献标志码:A 文章编号:2096-9902(2025)23-0066-05
DOI:10.20028/j.zhnydk.2025.23.015
Abstract:Toscientificallyassesstheeffectivenessandunderlyingmechanismsofintellgenttechnologyinagriculturalscienceeducationreform,thisstudyconstructsacausalanalysisframeworkbasedoncounterfactualcausalinferencetheoryemployingaquasi-experimentaldesignandmulti-sourcedataintegrationtechniques.Alongitudinalquasi-experimentaldesignwasimplementedwithexperimentalandcontrolgroups,utilizingdiference-in-diferences(DID)modelsandpropensityscorematching (PSM).Thestudyntegatsclassroobevatios,leaingeaviorlgsndcogitiveessmentstoevaluatetheesofinteligenttchnologonducationTersultsindicateateintegatinofintellgenttchnologysignificantlyehancestfciency of agricultural science education( β =7.6, P <0.01),comprehensively optimizes learning experiences (ES=O.85),and strengthens practical skill development( η2 =0.21).Multi-source evidence validation further demonstrates that students in the experimental group exhibit significantly higher knowledge transfer eficiency(t=5.32, p <0.001)and complex problem-solving ability( F =18.64, (2号 p<0.01 ).Thesefindingssuggesttatintellgenttechnologyefectivelyaddresssthetradionalbotleneckof"knowledgetoskil transformation"inagriculturaleducationthroughcognitivescafoldingconstructionandadaptivelearningpathoptimization.This studynotonlyestablishesacausalinferenceparadigmforevaluatingeducationaltechnologyefectivenessbutalsoprovidesevidence-based insights for the digital transformation of agricultural higher education.
Keywords:inteligent technology;agricultural education;causal inference;multiple evidencefusion;teachingreform
在高等农科教育人才培养中,教与学的主导和主动程度会直接影响农科院校本科生的培养质量。(剩余7610字)