草腐菌培养料发酵过程中理化性质和微生物群落的变化
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S646 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1673-2871(2025)09-187-12
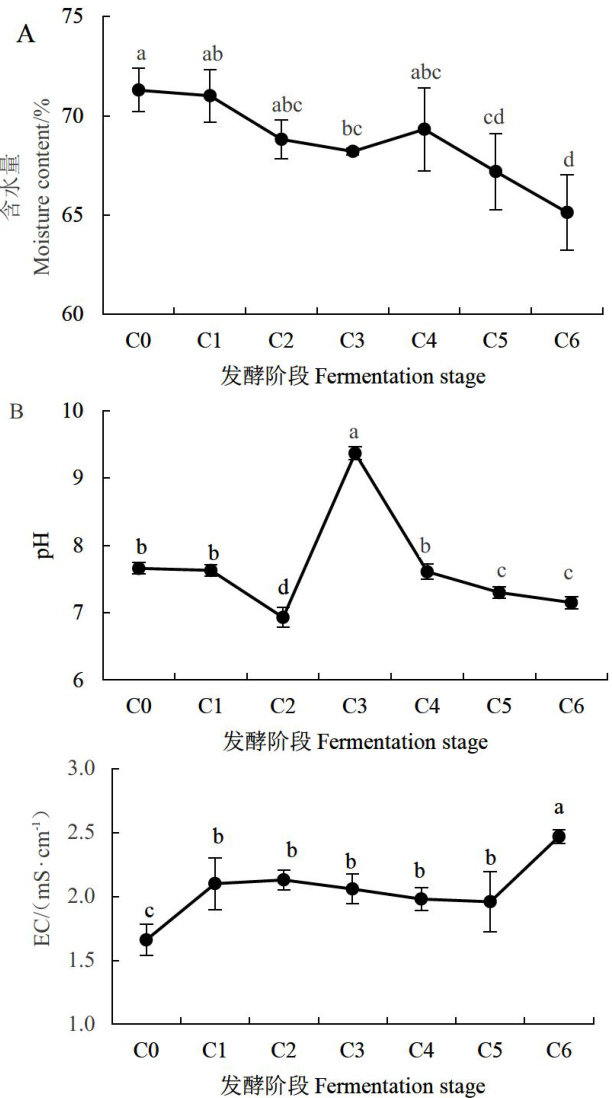
Abstract:Tooptimize the fermentation processof grass-decaying fungus culture medium and improve theeficiencyand quality of mushroom production,samples were collected at7 fermentationstages:unfermented(Co),after 4 turnings (C1,C2,C3,C4),completionof primaryfermentation(C5),andcompletionofsecondaryfermentation(C6)of grass rotfungusculturesubstrate.Thephysicochemicalpropertiesandlignocelulaseactivityoftheculture mediumweremeasured, andhigh-throughput sequencing technology was usedtodetectthe succession of microbial communities intheculture medium.Thecorelation between physicochemical properties and microbial communities was assessed at the OTU level. Theresults showed that during fermentation,the moisture(w,the same below)and pH of the substrate first decreased, then increased,and finally decreased again,reaching 65.14% and 7.15,respectively; the electrical conductivity showed a trend of increasing,then decreasing and then increasing,and finallywas 2.47mS⋅cm-1 ;the total organic carbon content (TOC)slightly increased in the C0-C1 stage,and then gradually decreased,and finaly was 45.04% ; and the total nitrogen content(TN) increased,then decreased and then increased,and finally was 0.63% ; Cellulase and xylanase activities wereinthe trendof decreasing,then increasing andthendecreasing,while laccse activityasa wholecontinued to decrease,remainingat 2.08,3.58,and 13.19U⋅g-1 ,respectively,at the end of fermentation.In the bacterial community, Thermus was thedominant genus intheC1-C6period,whilenorank_fnorank_o_SBR1031was thedominantgenus in the C2-C6 period.Mycothermus was thedominant genus at C1-C6 stage.TOCandTNwerethemost significantphysicochemical factors affecting bacterial and fungal community structure,respectively.
Key words: Grass rot fungi; Cultivation substrates; Physicochemical properties;Microbial community sucession
食用菌有草腐菌和木腐菌2种,属于草腐菌的双孢蘑菇、姬松茸和鸡腿菇生产上以发酵料进行栽培。(剩余21063字)