山东省老年人中医药电子健康素养现状及提升策略研究

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:R2-03 文献标识码:A 文章编号:2096-4110(2025)08(a)-0194-05
Study on the Current Situation and Improvement Strategies of Electronic Health Literacy of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Shandong Province
SUN Zhongyao,LI Chunqiao, YANG Chuntao (Shandong Collegeof Traditional Chinese Medicine,Yantai Shandong,,China)
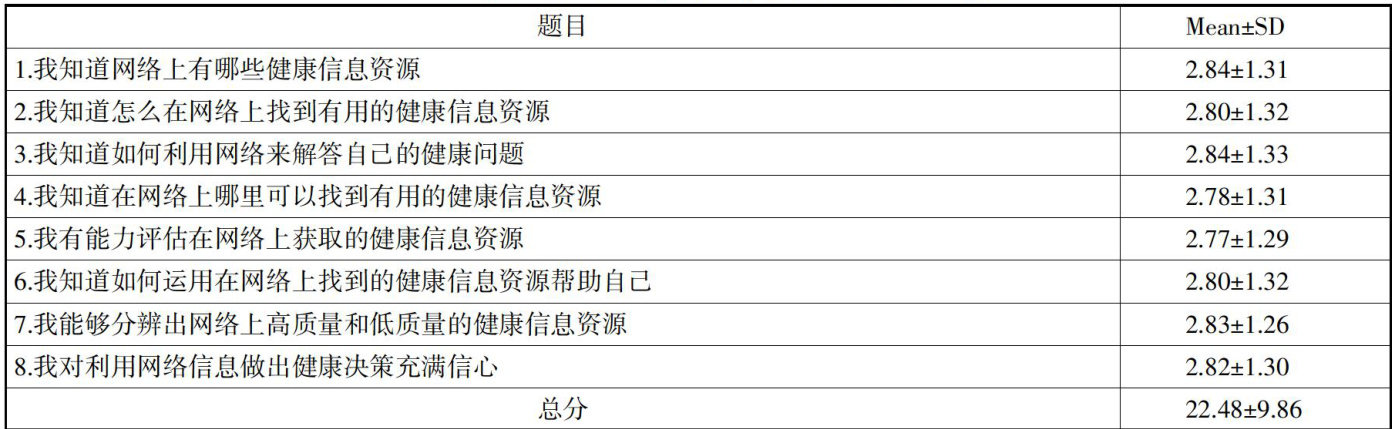
Abstract:This studyfocusesonthetraditional Chinese medicine (TCM)health needs of elderly people in ShandongProvinceundertheincreasingagingpopulation.Thestudyfocusesonthecurentsituationandimprovementpathofmedicalelectronichealthliteracy.Aquestionairesurveyandin-depth interviews wereconductedonelderlypeopleaged 6Oandabovein ShandongProvince throughsampling,andquantitativeanalysiswasconductedusing theeHEALSscaleandTCMhealthcultureliteracyquestioaire. Theresultsshowedthattheelectronichealth lieracylevelofelderlypeopleinShandongProvinceisrelativelylow(eHEALStotal score 22.48±9.86 ), and 63.13% of respondents are unable to effectively access online health information; the compliance rate of traditional Chinese medicine health culture literacy is only 30.00% ,with 42.39% of respondents scoring ⩽60 points. Insufficient knowledgereservescanasilyleadtomisleading medication;thelevelofiteracyissignfcantlycorelatedwithalthstatus.Among the group with high informationretrieval ability,83.69 % self-reported good health,while 66.4% of those with low ability suffer from chronicdiseases;thekeyinfluencingfactorsincludesocialsupportandtraditioalinformationacquisitionhabits.Basedothis,a four-dimensionalimprovmentstrategyisproposedindividualabilitytrainngtchnolgagingadptationtrasfoation,oliysupport,andculturalommunicationinovation,toprovidempiicalevidenceforptiizingthedigitaltransforatiooftditoalC
nesemedicine and assistingits integration into elderly health services.
KeyWords:Theelderly;E-health literacy;TCMe-health literacy;Current situation analysis; Improvement strategies; Shandong Province
近年来,山东省老龄化问题日益凸显。(剩余7102字)