睡眠障碍患者颈动脉斑块进展的超声动态监测

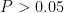
打开文本图片集
AbstractObjective:Toinvestigate therelationshipbetweensleepdisorders,especiallyObstructive SleepApnea(OSA)andcarotidplaqueprogresionandtoevauateitspotentialimpactofsleepdisordersoatheroslerosis.Methods:Atotalofpatints withsleepdisordersadmitedinthehospitalfromJune2O toJune2O24 wereincludedasthestudyobjects.Theyweredivided into an OSA group( n=70 ) and a non-OSA group( n=30 ) according to whether they were OSA patients.All patients underwent polysomnography(PSG)andthecarotid Dopplerultrasound scan beforetheenrollment andhad a6-month folowup.Therelationshipbetwensleedisordersandcarotid plaque progressionwasexploredbyanalyzingsleepmonitoringidicators,suchasapnea index(AHI),lowestbloodoxygenaturation,ndrsultsofcarotidulrasound,incudingplaquemorpholog,ie,tia-dia thickness(IMT),peak systolic velocity(PSV),etc.Results :The rate of carotid plaque area increase in OSA group( 60.00% )was significantly higher than that in non-OSA group 30.00% ) within 6 months and IMT and PSV of the observation group increased significantly. Multivariate regression analysis showed that the IMT increased by 0.15mm2 and PSV increased by 0.18 cm/s for every 1 time/h increase in AHI. For every 1% decrease in the lowest oxygen saturation,the IMT increased by O.1O mm². Conclusion:Sleepdisorders,especiallyOSA,arecloselyassociated withcarotidplaqueprogresion,andtherateofplaqueprogesin OSA patients issignificantlyhigherthanthatinnon-OSApatients.AHIandlowest oxygensaturationareimportantpredictors for carotid plaque progression.
KeywordsSleep disorders; Obstructive sleep apnea; Carotid artery plaque; Ultrasonic dynamic monitoring; Blood oxygen;Apnea index;lowest blood oxygen saturation;Arteriosclerosis
中图分类号:R338.63;R56 文献标识码:A doi:10.3969/j. issn.2095-7130.2025.04.020
睡眠障碍,尤其是阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停(Ob-structiveSleepApnea,OSA),已被认为与心脑血管疾病的发生密切相关[1]。(剩余3873字)