基于全身免疫炎症指数的机器人辅助骨盆前环INFIX固定术创伤评估

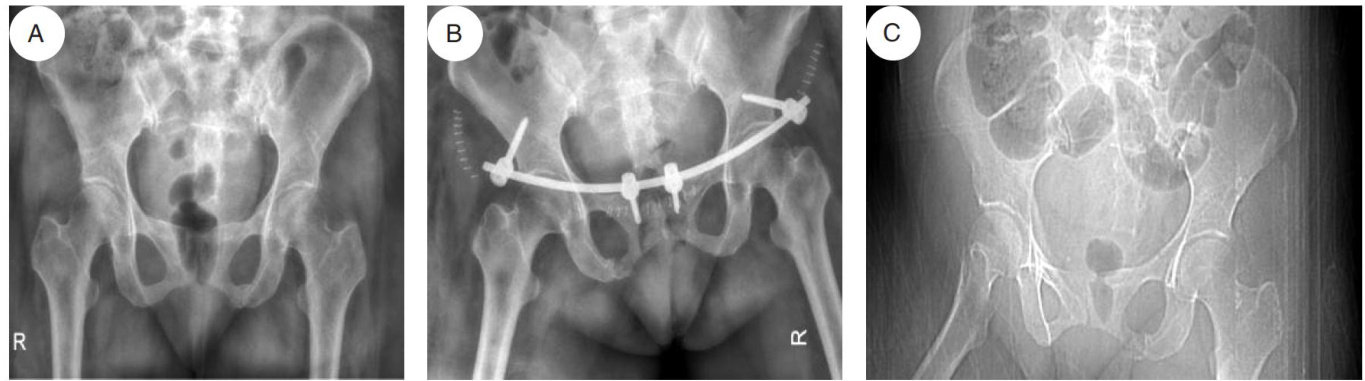
打开文本图片集
中图分类号 R687.3 R446.11 文献标识码A 文章编号 2096-7721(2025)08-1305-05
Assessment trauma in robot-assisted anterior pelvic ring INFIX fixation based on systemic immune-inflammatory index
ZHANG Yongtao, NIU Jing, HE Quanjie, LIU Huan, YANG Hailiang ( , University , ,)
AbstractObjective:Toexploretheapplicationvaluesystemicimmune-inflammatoryindex(SI) inevaluatingsurgicaltrauma inrobot-asistedintealfixation(INFIX)foranteriorpelvicingfractures.Methods:Aretrospectivestudywasconductedon41 patientswhounderwentINFIXfixationforanteriorpelvicingfracturesattheAfliatedUniversityEngieering from July 2O22 to December 2023.The patientswere divided into the robotic group (n=20) )and the non-robotic group (n=21) based on thesurgicalapprachiferenceingnder,geperationtie,bloodlo,omplicationatesdSIrecompedetweenth two groups.Results:No statistically significant diferences were observed in genderor age between the two groups ( Pγ 0.05). Compared tothe non-roboticgroup,therobotic grouphadshorteroperativetime,lessbloodlossandfewercaseslateralfemoralcutaneous nerve palsy (P<0.05) .Postoperative SII increased in both groups,but the non-robotic group showed significantly higher SI ( P <0.05). Conclusion:omparedtoaditioalallyiasivesurgeryobotastedIfxationfoanteriorelvicingfracureause less trauma.SI can serve as areliable immune-inflammatory indicator for quantifying surgical trauma severity.
KeyWordsRobot-assisted Surgery;Systemic Immune-inflammatory Index;InteralFixation; Minimall Invasive Surgery
骨盆环损伤在全身骨折中仅占 1.5%~3.9% ,但其发病率和死亡率却显著高于其他骨折类型]。(剩余10259字)