一起由副溶血性弧菌引起的食源性疾病暴发事件的调查与分析

打开文本图片集
Investigation and Analysis of AFoodborne Disease Outbreak Caused by Vibrio parahaemolyticus
CHEN Hui, ZENG Yuehong (Mianyang High-tech Zone Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Mianyang 621oo0, China)
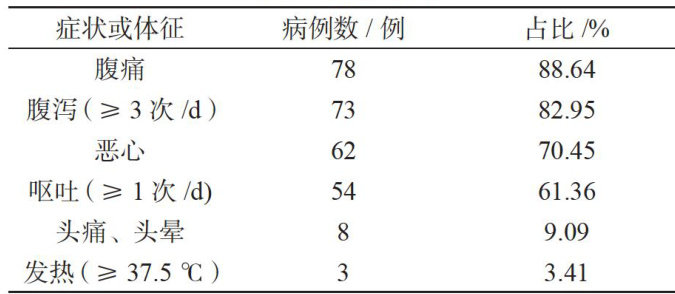
Abstract: Objective: To investigate and analyze a foodborne disease incident and provide references for preventing such incidents.Method: Through on-site epidemiological investigation,food hygiene asessmentand laboratorytesting,thesuspectedfood,pathogenicfactorsandpolutionsources were systematicallidentified.Result: A total of 88 cases were confirmed in this incident, with a prevalence rate of 26.67% (88/330). The main symptoms were abdominal pain (88.64%) ,diarrhea (82.95%) ,nausea (70.45%) and vomiting (61.36%) ,with an average incubation periodof11.5 hours (ranging from5 to 30 hours).Vibrio parahaemolyticus was isolated from l8 case specimens and 3chef's anal swab specimens,and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis molecular traceability analysis was conducted. The results showed that the DNA fingerprint patterns of the above samples were 100% similar. Conclusion:This incident was caused by food contamination due to Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection of the chef. It is recommended that regulatory authorities strengthen supervision and implement training mechanisms for food industry personnel to prevent similar incidents.
Keywords: Vibrio parahaemolyticus; foodborne disease events; field epidemiology; pathogenic factor
副溶血性弧菌是一种嗜盐细菌,被认为是引发食源性疾病的重要致病菌[1],主要分布于环境水体和海产品中[2],对人和动物均有较强的毒力。(剩余5765字)