高地温引水隧洞施工通风降温数值模拟研究

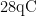
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:U455 文献标志码:A 文章编号:2095-2945(2025)18-0050-08
Abstract:Toaddressthegeothermalhazardinwaterdiversion tunnels,numerical simulationswereconductedusingthe COMSOLMultiphysicstoinvestigatethechangesiinteraltemperatureduringtunnelventilation.Theefectsofvariousfactors, includingdiferentventltionspeeds,ventilaiontemperatures,surroundingrocktmperatures,anderalinsulationlars,othe coling performanceof tunelventilationwerestudied.Thecalculationresultsindicatethatwhen theairtemperatureissetat 5% and 15qC ,the ambient temperature within the range of 10~30m behind the tunnel face can be reduced to below 28‰ within half an hour of ventilation.After two hours of ventilation,using a lower airflow velocity ( v =0.5 m/s) can reduce the overall tunnel temperature to a level close to that achieved with a higher airflow velocity( u =0.9 m/s). When the surrounding rock temperature reaches 60% ,except for the area 10m behind the tunnel face,the temperatures at farther locations can be reduced to below with sufficientventilation time.With theapplicationofthermalinsulation layers,thetemperaturereductionsat 10m and 30m can further reach 41.1% and 14.0% ,respectively. The research results can provide reference for controlling high -temperature heat damage in diversion tunnels.
Keywords:diversion tunnel;ventilationandcoling;numerical simulation;heat insulationmeasures;highland heathazard
随着我国工业化和城镇化进程的持续推进,国民日益增长的生存发展渴望以及对资源开发利用的迫切需求,已成为推动能源结构优化调整和加速基础设施建设的强劲动力。(剩余8225字)