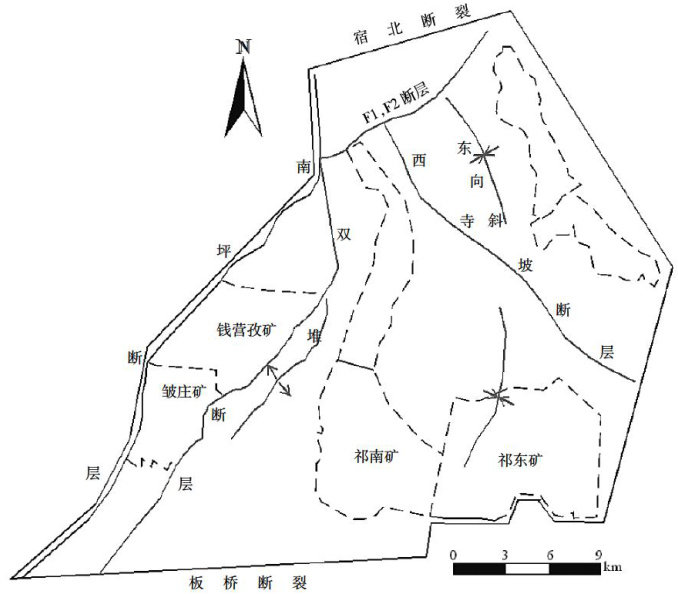
祁南煤矿某采区新生界含水层与隔水层分布特征及其水力联系分析

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:P641 文献标志码:A 文章编号:2095-2945(2025)19-0097-04
Abstract:Minewater,aprimaryconcernincoalresourceextraction,posesasignificantthreat toconstructionsafety.The coal-bearingstrataintheQinanminingareaarecoveredbyathickandlooselayerofCenozoicsedimentsstoringgroundwater. ThisstudyexploresthehydrogeologicalconditionsoftheCenozoiclooselayerinaspecificminingareaoftheQinancoalmine, focusingonthedepthanddistributionofancientiverchannelswithintheCenozoic.Utilizingregionalgeologicaldrilingdataand loginginformationanaalysisftelitholgyofCenozicsdimentsisonductedaquifes/aquitardsarecategorizedandtir hydraulicconnectionsarediscussed.TheinvestigationrevealsthepresenceoffouraquifersandthreeaquitardsintheCenozoic loselayer.Thefrstaquiferexhibitscharacteristicsofacompositepore-typegroundwatertoaweaklypresurizedaquiferwhile thelowerthreeaqifersareidentifiedaspressrizedaquifers.Ananalysisofhydraulicconnectionsidentifiesthewidespreadand stableditributionofthethirdaquifer,leadingtothelossofhydraulicconnectionsbetweetheupperaquiferandthefourth aquifer.Asaresult,theupperaquiferhasnodirectimpactonminerecovery.Waterfromthefourthaquiferinfitratesthemine throughfracture zones,establishing itas the primarysourceof waterdamage for shalowcoal mining under bedrock.
Keywords:Qinan coal mine; aquifer; aquitard; hydraulic connection; confined aquifer
煤炭是我国的重要基础能源,巨大的需求量也促使煤矿的开采规模与日俱增。(剩余4826字)