获得性免疫缺陷综合征(AIDS)患者合并肝损伤的危险因素及机制

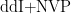
打开文本图片集
Abstract:Withtheadventoftheeraofantiretroviraltherapy,thelifespanofindividualslivingwithhumanimmunodeficiencyvirus (HIV)infectionhasbeenextendedsignificantly,andthereisasignificant increaseintheincidencerateof non-acquired immunodeficiency syndrome(AIDS)-related diseases,among which liver diseaseisoneof the maincausesof non-AIDS-related deaths.ThereisstillarelativelyhighincidencerateofiverinjuryinpatientswithHIVinfection,andtherearevariouscausesof liverinjury.TisarticlereviewsthepossbleriskfactorsforliverinjuryandrelatedmechanismsfromtheaspectsofHVinfection, co-infectionwithhepatitisBvirus/hepatitisCvirusandotherpathogens,drugs,metabolicdysfunction,andintestinalbacterial translocation,in order to provide a reference for the management of individuals with HIV infection.
Key Words:HIV;Acquired ImmunodeficiencySyndrome;ChemicalandDrug InducedLiver Injury;HepatitisViruses;NonalcoholicFattyLiverDisease
Researchfunding:KeyR&D PlanofShandongProvince(2O21SFGC0504)
在抗逆转录病毒治疗(antiretroviral therapy,ART)时代到来之前,人类免疫缺陷病毒(human immunodeficiencyvirus,HIV)感染者主要死于获得性免疫缺陷综合征(acquired immunodeficiency syndrome,AIDS)相关疾病,如机会性感染及肿瘤;而ART的普及使得非AIDS相关死亡率相对升高[1],且因肝脏疾病入院的人数呈上升趋势[2]。(剩余18788字)