炎症性肠病合并自身免疫性肝病

打开文本图片集
Abstract:The coexistence of inflammatory boweldisease(IBD)andautoimmune liver disease(AILD)hasgained increasing atentioninclinical practice,andthereare significantincreasesintheprevalenceratesofautoimmune hepatis(AIH),priary sclerosing cholangitis(PSC),andAIH-PSCoverlapsyndrome among the patients with IBD.Several pathogenic mechanismsare shared between IBDandAILDs,including geneticsusceptibility,dysregulationofthegut-liveraxis,immune imbalance,and abnormalbileacidmetabolism.TheECCOguidelinesrecommendthatpatientswhoaresuspectedofIBDandreceivenotreatment shouldundergoaseriesof liver function tests,including alanineaminotransferase,alkaline phosphatase,gamma-glutamyl transferase,and totalserum bilirubin,aswellasregularrexaminations during follow-up.WhileIBD-AILDpatients haveunique clinicalfeatures,thereisstillalackofuifieddiagnosisand treatmentguidelinesforthiscomorbidity,andtheselectionof therapeuticgoaloftenentailsacarefulbalancebetweentheintestinaltractandtheliver,requiringinterdisciplinarycolabration andcombined therapiesbasedonpathogenesis.Futureresearchshouldfocusonthedynamicregulatorynetworksof thegut-liver axis to develop innovative intervention strategies that ensure both efficacy and safety.
KeyWords:Autoimmune Diseases;Inflammatory Bowel Disease; Therapeutics
Research funding:Health Research & Special Projects Grant of China(2O1502005)
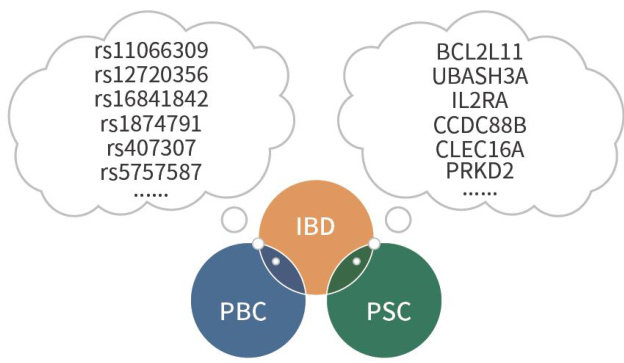
1背景与流行病学
由遗传、环境、免疫因素等相互作用引起的慢性复发性肠道炎症性疾病[1],主要包括克罗恩病(crohn disease,CD)和溃疡性结肠炎(ulcerativecolitis,UC)。(剩余15794字)