光学导航定位系统辅助CT引导肺结节穿刺定位的应用及穿刺后气胸的影响因素分析

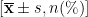
打开文本图片集
中图分类号 R655.3 文献标识码 A 文章编号 2096-7721(2025)07-1090-08
AbstractObjective:Toevaluate theclinicalutilityofopticalnavigationsystem-asisted CT-guided pulmonarynodule puncture positioning before video-asisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS)and analyze factors influencing post-puncturepneumothorax. Methods: Aretrospective analysis wasconductedon104 patientswhounderwent CT-guided Hook-wirelung nodule puncture positioning before VATSat theThirdPeople'sHospitalofChengdufromJune2023toDecember2O23.Patientsweredividedintothenavigation group ( n =51,receiving optical navigation-assisted CT-guided localization)and the conventional group( n :53,receiving standard CT-guided localization).Clinicaldataofpatietsrecompaedbetweetetwogoups,andmultivarateLgisticegesionasedtodtify pneumothoraxriskfactors.Results:Thenavigationgroupshowedshorterminimaldistancebetweenthepositioningwireandthenodule, higherfirstattsucssatndhedosgthpoduct(D)tanthonentioalgop(5).Nosigificatdn pneumothorax or pulmonary hemorrhage rates was observed between the two groups (P>0.05) . Multivariate analysis revealed that increased neededepthitoenggaterhstalltcknsstradyededfiptsueseproteiecst pneumothorax,whileneedleproxiitytoribs wasariskfactor.Conclusion:Opticalnavigation-asisted CT-guded pulmonarynodule puncture positioning issafeandefective,whichhas higherpunctureprecisionthanconventionalpuncture.Clinicalyoptimizing path planning usingthenavigationsstem'saccuracyavidingiproxiityandesuringfistateptsuccsscanniizepooax risks and enhance procedural safety.
KeywordsOpticalNavigationandPostioingSystem; ComputerTmogaphy;PulmonaryNodules; PuncturePositioning;Pneumothorax
随着健康意识的增强和低剂量胸部CT在常规体检项目中的普及,越来越多难以定性的肺小结节被检出[1。(剩余11794字)