赤羽病病毒与宿主相互作用机制研究进展

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S852.65 文献标志码:A 文章编号:0366-6964(2025)10-4877-12
Abstract: Akabane virus (AKAV) is a vector-borne pathogen that primarily causes reproductive disorders in ruminants such as catle and sheep. It is widely distributed in areas where bloodsucking insects such as mosquitoes and midges are concentrated in tropical and temperate regions. The infection situation is particularly severe in some Southeast Asian and East Asian countries. Regional epidemics have been found in China. With the increasing intensification of cattle and sheep farming,frequent trading and transportation,and the expansion of the breeding range of vector insects due to climate change,the disease has a further trend of spreading infection. In this paper,beginning with pathogenic characteristics and tissue tropism of AKAV,the interaction mechanisms between virus infection and the host's responses were summarized emphatically. It could provide a reference for further exploration of the pathogenesis of AKAV and the development of corresponding therapeutic drugs and preventive preparations.
Keywords: Akabane virus; pathogenic mechanism; viral replication; interferon;apoptosis∗ Corresponding author: ZHAO Guangwei, E-mail: zhaoguangwei@swu.edu.cn
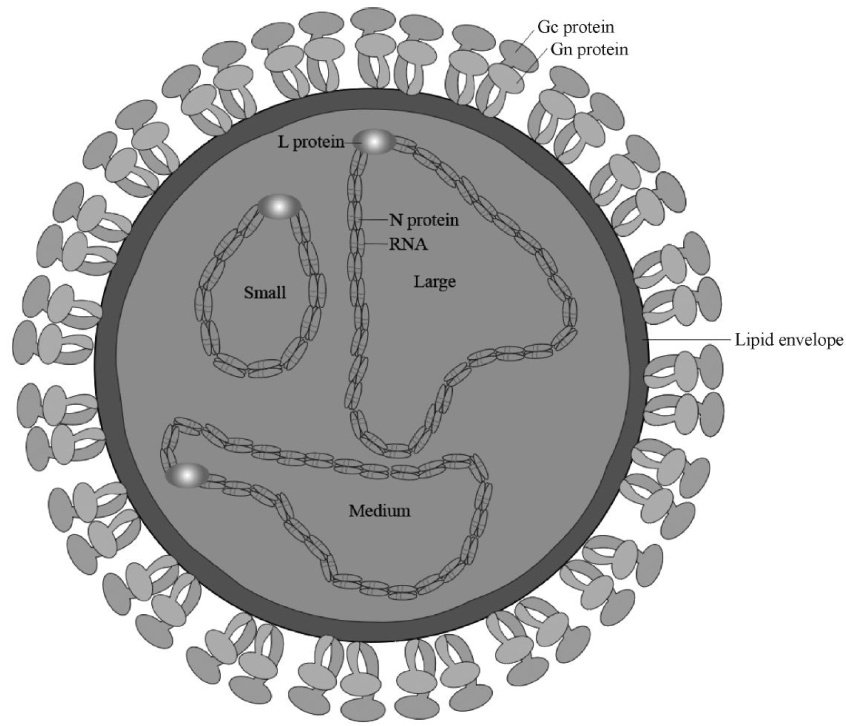
赤羽病又称阿卡斑病(Akabanedisease,AKAD),是由赤羽病病毒(Akabanevirus,AKAV)引起的一种虫媒性传染病,可由库蠓、蚊等吸血昆虫传播,主要引起牛、绵羊、山羊、骆驼等反刍动物发病[1-2],以流产、早产、死胎、胎儿畸形[3]、木乃伊胎、新生胎儿发生关节弯曲和积水性无脑综合征[4-5]为主要特征。(剩余22940字)