果树-菌菇间种系统对病虫害综合抑制效应的研究

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S436 文献标志码:A 文章编号:2096-9902(2025)12-0027-05
Abstract:Toevaluate thecomprehensiveinhibitoryefectsofapple tree-mushroom intereroppingonmajorapplepestsand diseases,arandomizedblock designwasimplementedwith threetreatments:apple monoculture,aple-mushroomintercroping, andmushroommonoculture.Thestudymonitoredthediseaseindexofappleanthracnose,fruitinfestationrateoftheoriental fruit moth,andmoldcontaminationrateofmushrooms,whileanalyzingsoilphysicochemicalproperties,enzymeactivities,microbial communitycharacteristics,aswellasplantdisease-resistantenzymeactivtiesandfruitquality.Resultsdemonstratedthat intercropping significantly reduced the apple anthracnose disease index (by 39.9% ),oriental fruit moth infestation rate (by (20 40.9% ),and mushroom mold contamination rate(by 42.8% ).Concurrently, soil organic matter and nutrient content increased, enzymeactiesimproved,microbialdiversityhancedandtherelativeabundnceofbenefcialmicroorganismsoseAle tresexhibitedheighteneddisease-resistantenzymeactivitiesandimprovedfruitquality.Thefindingsindicatethatapplemushroomintercropingffectivelysuppresesaplepestsanddiseases,enhancessoilhealthandcropquality,demonstrating significant potential for widespread adoption.
Keywords: fruit tree;mushroom; intercropping;disease and pest; soil environment
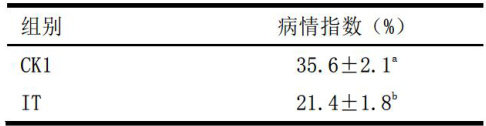
果树产业在全球农业中占据着重要地位,为人类提供丰富的营养和经济收益。(剩余6826字)