牙隐裂伴牙髓病变患者经根管治疗后远期效果评价及其影响因素分析

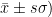
打开文本图片集
Evaluation ofLong-term Effectand Analysis of Influencing Factors inPatientswith Cracked Tooth Accompanied Dental Pulp Lesionsafter Root Canal Treatment/HOU Shujia.//Medical Innovation of China,2025,22(17):153-156
[Abstract]Objective:To analyze the long-term efficacyand influencing factors ofpatients with cracked tooth accompanied dental pulp lesions after rootcanal treatment.Method:Aretrospective analysis was conducted onthe clinical data of 1O4 patients with cracked toth accompanied dental pulp lesions admited to Lianyungang Municipal Oriental Hospital from March 2O2O to March 2O23.Allof them underwent root canal treatment and were followedup for one year after treatment to observe the therapeutic efect.In addition,information such as the age and gender ofthe patients wascollected to explore therelevantfactorsafecting the long-term efficacyof root canal treatment.Result:Among the 1O4 patients,a total of 13 cases (12.50 % ) failed in treatment and 91 cases (87.50 % ) succeeded.In the failure group,the proportions of patients with crack depth reaching the botom ofthe pulp, probing depth >5 mm,lack of vitalityofthe dental pulp,and periapical lesions wereallhigher thanthose in thesuccess group,the differences were statistically significant( P <0.05). logistic regression analysis showed that crack depth reaching thebottom of the pulp,probing depth >5 mm,lack of vitality of the dental pulp,and periapical lesions were independentrisk factors forthefailureof patients withcracked toothaccompanied dentalpulplesions afterrootcanal treatment ( P <0.05). Conclusion: The crack depth reaching the botom of the pulp,the probing depth >5 mm, the lackof vitalityof thedental pulp,and the presenceofperiapicallesionsare independentriskfactors forthefailureof patients with cracked toothaccompanied dental pulp lesions after rotcanal treatment,individualized intervention can be guided based on this during clinical treatment to improve prognosis.
[KeyWords]Cracked toothDental pulp lesionsInfluencing factorsUnderlying diseasesPeriapical lesions
First-author'saddress:Department of Stomatology,Lianyungang Municipal Oriental Hospital, Lianyungang222042, China
牙隐裂属于牙齿折裂的一种,常在中老年群体内发病,临床患病率较高,为 34%~74%[1-2] 。(剩余5151字)