上海地下水回灌优化防控地面沉降策略研究

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:P641.8;P66 文献标志码:A 文章编号:2095-1329(2025)03-0062-06
Abstract:Landsubsideneis teprimarygeologicalhazardinSanghaiposingalong-temserousthreattourbansafetyandustaiable socioeconomicdevelopment.Althoughthesubsidenceratehas notablydecreased,unevensubsidenceremains prominent,demanding increasinglypreciseontroland preventionmeasures.Currntlygroundwaterextractionandrecargeareunevenlydistributedacross regions andaquiferlayers,with localized groundwater depresion cones persisting incertainareas.The existing extraction-recharge paterstillfails tometsubsidencecontrolrequirements.Thisstudyconductsanin-depthanalysisoflong-termgroundwaterand subsidencemonitoringdatainSangharoposinganotiizedgroundwaterchargsheme.Usingare-dimensionalgroudater sepageandon-dimensioalsubsdenecoupledmathematicalmodel,tesheme'sefectivenes initigatingsbsidencesalidated. Results indicate that reducing total annual recharge volume by 5% while strategically shifting recharge focus toward general subsidence controlzonescanachevesubsidencemanagementtargetshileoptizingresourceallcation.Tisoptizedapproachprovidescitical decision-making support for precision subsidence control and prevention.
Key Words:and subsidence;precision preventionandcontrol; groundwaterartificialrecharge; preventionandcontrolstrategy
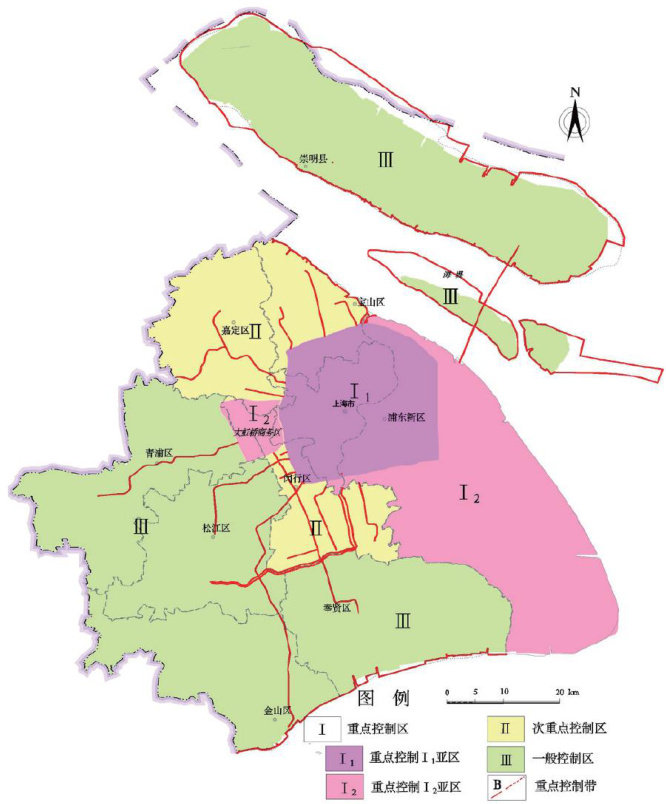
地面沉降作为全球性地质灾害[1-2],长期以来严重威胁着沿海城市安全和经济社会可持续发展[3],也是上海地区最主要的地质灾害。(剩余8289字)