不同通气模式在ARDS病人中应用效果及预后分析

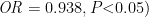
打开文本图片集
[关键词] 呼吸窘迫综合征;呼吸,人工;血流动力学;预后;影响因素分析 [中图分类号] ; [文献标志码] [文章编号] ( ) doi:10.1712/ms.2096-532.2025.61.063
[Abstract] Objective Toinvestigatetheaplicationefectofdiferentventilationmodesinpatientswithacuterespiratory distres syndrome(ARDS)andtheirimpactonprognosis. Methods Atotalof162ARDSpatientswhoatendedSecondPeople’sHospitalofLuoheCityfromJanuary2020toFebruary2023wereenroledandrandomlydividedintoobservationgroupand controlgroup,with81patientsineachgroup.Thepatientsintheobservationgroupreceivedpresure-regulatedvolumecontrol ventilation(PRVC),whilethoseinthecontrolgroupreceivedsynchronizedintermitentmandatoryventilation (SIMV).Related indicatorswerecomparedbetwenthetwogroups.Acordingtothesurvivalstatusofpatientsonday21afterenrolment,they weredividedintosurvivalgroupanddeathgroup,andtheLogisticregresionanalysiswasusedtoinvestigatetheasociationbetwenventilationmodeandprognosis. Results Afterintervention,bothgroupshadasignificantincreaseinarterialpartialpressureofoxygen ⋅t=34.412,44.908,P<0.05) )andasignificantreductioninarterialpartialpresureofcarbondioxide PaCO2 ) ⟨t= 16.116,8.430,P<0.05) ),andcomparedwiththecontrolgroup,theobservationgrouphadasignificantlylower PaCO2 afterintervention (t=7.908,P<0.05) ).Comparedwiththecontrolgroup,theobservationgrouphadasignificantlyshorterventilationtime andsignificantlylowernumbersofsputumaspirationproceduresandventilatoralarms (t=7.183-9.419,P<0.05) ).Anincreasein age ⟨OR=1.199,P<0.05) ),anincreaseinAcutePhysiologyandChronicHealthEvaluation I score ⟨OR=1.813,P<0.05⟩ ),and areductioninoxygenationindex )increasedtheriskofdeath,andcomparedwithSIMV,PRVCreducedthe riskofdeath ⟨OR=0.162,P<0.05) ). Conclusion PRVCcanincreaseventilationeficiency,improverespiratoryparameters, andreducetheriskofdeathinARDSpatients.
[Keywords] respiratorydistres syndrome;respiration,artificial;hemodynamics;prognosis;rotcauseanalysis
急性呼吸窘迫综合征(ARDS)是一种因肺泡和微血管通透性障碍导致的严重炎症反应,表现为急性呼吸困难、低氧血症和肺部浸润,常伴发热、心率增快、高碳酸血症等,易引发多器官功能障碍综合征和死亡[1-2]。(剩余5464字)