5种黄精属植物叶片的生理生化与显微、超微结构研究

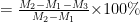
打开文本图片集
[中图分类号]R282.5 [文献标志码]A [文章编号]doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-070X.2025.11.010
[Abstract]Oectieudateilogical,ocalosruuraldlsuctalactestic fromfivePolygonatumspecies.MethodsLeavesfromfivewidelycultivatedPolygonatumspecies(P.odoratum,P.sibiricum,P. cyrtonem,P.ingianum,andP.nanense)weresedasexperimentalaterials.Leafaterontent,corophyllontentubisO enzymeactivityweremeasured,andleafmicrostructuralandultrastructuralfeatureswereobservedResultsTheleafwaterontent of shade-cultivated P. sibiricum, P.cyrtonema, and P. kingianum (78%~81 % )was significantly higher than that of non-shaded P. odoratum ( 73% , P<0.01 ).Shade-cultivated Polygonatum species showed higher total chlorophyll content (CT),chlorophylla (Ca), andchlorophyllb(Cb)contentcomparedtonon-shadedP.odoratum.However,theCa/Cbratioof non-shadedP.odoratumwas higherthan thatofseveralshade-cultivatedPolygonatumspecies.P.kingianumexhibitedthe highestRubisCOactivity (413.78U/L), whileno statistically significantdifference (P>0.05) wasobserved in RubisCo activitybetween shaded and non-shaded P.odoratum (294.54U/Land89.58Urespectively)MicrostructuralobservationrevealedthatnonshadedP.odoratumexhibitedthethickest leaves(248.77μm),with greater lengthandwidthofboth upperandlowerepidermalcelscompared toothershade-cultivated Polygonatum species.In contrast,P. kingianum showed the thinnest leaves 113.60μm )andthe smallest lower epidermal cells (27.13 μm in length × 20.90 μm in width). Ultrastructural analysis indicated that shade-cultivated P.odoratum contained chloroplasts with welldevelopedthylakoidsandregularlyshapedosmiophilicgranules,whereasnon-shadedP.odoratumdisplayeddegenerated thylakoidsdgedooliales.uireriniolcalcaloal andultrastructuralcharacteristicsamongthefivePolygonatumspecies.Field-grownP.odoratumposseses thickerleaves,larger epidermalcels,andahigherCa/Cbratio,whereasshade-cultivatedPolygonatumspeciesmaintainrelativelyhigherleafwater contentandchlorophyllcontentbutalowerCa/Cbratio.Thisstudyprovidesvaluableinsightsforevaluatingthephotosynthetic characteristics and environmental adaptability of Polygonatum species.
:ywords]Polygonatum;shade cultivation; physiological and biochemical characteristics;microstructure;ultrastru
黄精属(Polygonatum)是百合科(Liliaceae)重要的多年生草本资源,《中华人民共和国药典》中收载了4种黄精属药用植物,分别为:黄精(Polygona-tum sibiricum Red.)多花黄精(Polygonatum cyrtone-ma Hua)、滇黄精(Polygonatum kingianum Coll.etHemsl.)和玉竹[Polygonatum odoratum (Mill.) Druce],其肉质根茎为传统中药材,药食两用。(剩余10194字)