弓形虫TR与ROP5双基因缺失株的构建及其生物学功能研究

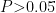
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S852.729 文献标志码:A 文章编号:0366-6964(2025)07-3408-15
Abstract: To explore whether the TR and ROP5 of Toxoplasma gondii have a synergistic effect on anti-host ROS damage,we used CRISPR/Cas9 technology in this study to successfully obtain the TR and ROP5 double gene knockout strain (TR-ROP5-KO). By biological activity analysis, we discovered that the invasion,proliferation ability in vitro,and virulence in viuo of TR-ROP5- KO strain were lower than those of RH strain,TR gene deletion strain ( TR -KO)and ROP5 gene deletion strain (ROP5–KO) .These results indicated that the simultaneous deletion of TR and ROP5 in Toxoplasma gondii not only lead to a decrease in the viability of the parasites in vitro cells, but also reduce the virulence of toxoplasma in the host. The results of the oxidative stress levels of T . gondii and their effects on ROS levels in mouse macrophages cells showed that the level of oxidative stress induced by TR-ROP5-KO strain was significantly higher than by RH strain ( P<0.05) ,but there was no differences relative to TR single gene deletion strain ( P>0.05 .ThemRNA levels of NF-κB , IL-12 and IFN- ⋅γ in mouse macrophages infected with TR/ROP5 single and double gene deletion strains were detected by RT-qPCR,and the levels of IL-12 in serum of mie was also detected by ELISA. The results suggested that the TR-ROP5- KO infection group was significantly higher than RH group ( (P<0.05 ),but the TR-ROP5-KO infection group was not significantly higher than the TR -KO infection group ( P>0.05 ).The results indicated that TR and ROP5 genes have no synergistic effect on resisting the ROS damage of host. In this study,the method of constructing double-gene deletion strains of TR and ROP5 showed that the two genes had no synergistic effect on the anti-ROS damage of the host,which provided the method basis for the subsequent research on the function of multiple genes of Toxoplasma gondi and the basic material for the research on the immune escape mechanism of Toxoplasma gondii.
Keywords: Toxoplasma gondii;CRISPR/Cas9;TR;ROP5;ROS ∗ Corresponding author: WANG Quan,E-mail: wangquan@shvri. ac. cn
刚地弓形虫(Toxoplasmagondii)是属于顶复门的一种专性细胞内真核寄生虫[1],由弓形虫感染引起的弓形虫病为人畜共患病,弓形虫的中间宿主繁多,除了感染温血脊椎动物和鸟类外,还感染全球三分之一的人口[2]。(剩余24330字)