磷脂酰乙醇胺对出生后生长迟缓仔猪结肠黏膜屏障功能和肠道菌群的影响

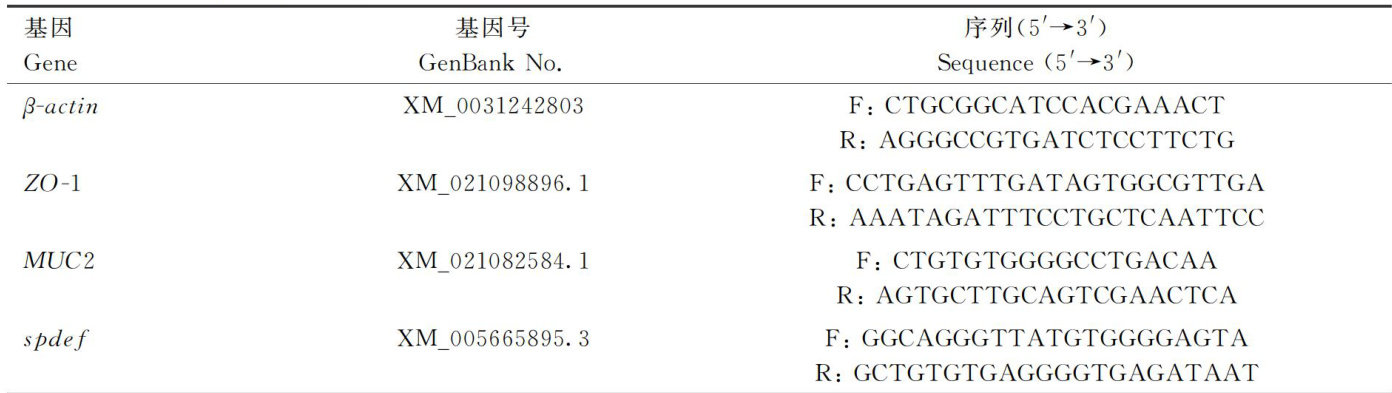
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S857.3 文献标志码:A 文章编号:0366-6964(2025)07-3305-11
Abstract: The aim of this study was to explore whether phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) could improve the colonic mucosal barrier function and alleviate gut microbiota disorder of postnatal growth retardation (PGR) piglets. At the age of 7 days,16 PGR piglets (average body weight 1.88±0.40kg) and 16 normal body weight(NBW) piglets(average body weight 2.79±0.50kg ) were randomly divided into 4 groups: CON-NBW(CN) group,PE-NBW(PN) group,CONPGR(CP)group and PE-PGR(PP) group,with 8 replicates in each group and 1 piglet in each replicate. The piglets in PN and PP groups were fed with 0.78gPE per day during lactation and 2.11g PE per day after weaning. The piglets in CN and CP groups were fed with equal volume of 0.9% saline. All piglets were weaned at 28 days of age and the experiment lasted for 42 days. The piglets were slaughtered at 49 days of age,and the colonic tissues and contents of piglets were collected for the determination of colonic mucosal barrier function related indicators and l6S rDNA sequencing of colonic contents. The results showed that compared with NBW piglets,the colon morphology of PGR piglets was damaged,and the number of goblet cels, the mRNA expression of ZO -1,spdef and MUC2 were significantly decreased ( ⋅P<0. 05 .At the same time,the piglet status (NBW or PGR) and PE treatment had a significant impact on the β (204号 diversity of colonic microbiota in piglets ( ⋅P<0. 05 ). The ratio of Firmicutes and Bacteroides,the relative abundance of Actinobacteria,Macrosphaera and Gemmiger in the colon of PGR piglets were significantly lower than that of NBW piglets,while the relative abundance of Proteobacteria was significantly higher than that of NBW piglets ( ⋅P<0. 05 ). PE supplementation alleviated the colonic morphological damage of PGR piglets, promoted the differentiation of colonic goblet cells and the secretion of MUC2,and increased the relative abundance of butyric acid producing bacteria in the colon ( P<0.05) .Therefore,PE improved the mucus synthesis and secretion function and alleviated gut microbiota disorder of PGR piglets.
Keywords: phosphatidylethanolamine;postnatal growth retardation; colon;gut microbiota; piglets∗ Corresponding author: HE Lingyun,E-mail:15116380334@163.com
微生物的早期定植影响肠道营养物质吸收和屏障功能等,对仔猪肠道发育和机体生长至关重要[1]生长迟缓与环境因素、微生物早期定植、免疫系统发育、病原菌感染和母体营养水平等有关,可分为宫内生长迟缓(intrauterinegrowth retardation,IUGR)和出生后生长迟缓(postnatalgrowthretardation,PGR)[2-3]。(剩余17311字)