经尿道前列腺钬激光剜除术后低体温风险预测模型:基于逻辑回归、决策树和支持向量机

打开文本图片集
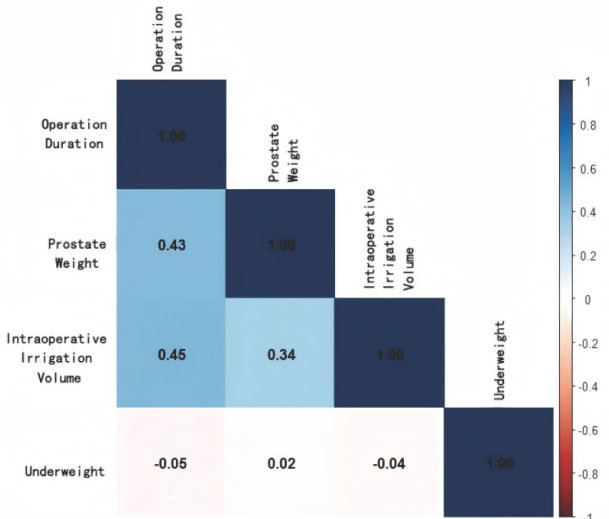
Abstract:ObjectiveTodevelopriskpredictionmodels forpostoperativehypothermiaaftertransurethral holmiumlaser enucleationofthe prostate (HoLEP)using machinelearning algorithms.Methods Weretrospectivelyanalyzed theclinical data of 403 patients from ourcenter (283 patients inthetrainingsetand120intheinternalvalidation set)and120patientsfrom Weifang People's Hospital (astheexternal validationset).Theriskprediction models werebuiltusinglogisticregression, decisiontreeanduportctoracine (S)andmodelformancesealatedintesofcracyecallisio F1 score andAUC.ResultsOperationduration,prostate weight,intraoperative irigation volume,andbeingunderweight wereidentifiedasthepredictorsofpostoperativehypothermiafollwingHoLEP.Amongthe3algorithms,SVMshowedthe bestprecisionrateandaccuracyinallthe3datasetsandthebestareaundertheROC(AUC)inthetrainingsetandvalidation set,followedbylogisticegessionicdasiilarUCinthtwoatasets.outpefoedlogisticgnd decisiontresiiscyalldellil validationset withbeterprecisionrateandaccuracythanlogisticregresionanddecisiontreemodelsbutslightlylowerrecall rate,F1ndendAUueanthisioteeoeltpfoedloisticessodeisitrelsin precisionacyoredAUintigetutdlightlwallateatisiotree.Co Among the3 models,SVMhas the best performance and generalizabilityfor predicting post-HoLEP hypothermia risk to provide support for clinical decisions.
Keywords: prostate;hypothermia; risk factors;machinelearning;predictionmodel
良性前列腺增生(BPH)作为中老年男性群体中的高发疾病,源于前列腺过渡区及尿道周围区域上皮与纤维肌性组织的无序增生,致使前列腺腺体良性增大,进而压迫尿道,引发下尿路症状(LUTS),涵盖尿频、尿急、夜尿等典型表现,严重干扰患者正常生活作息,极大降低生活质量[1-3]。(剩余10349字)