原发性肝癌患者的临床结局与治疗反应预测模型:基于失巢凋亡和免疫基因

打开文本图片集
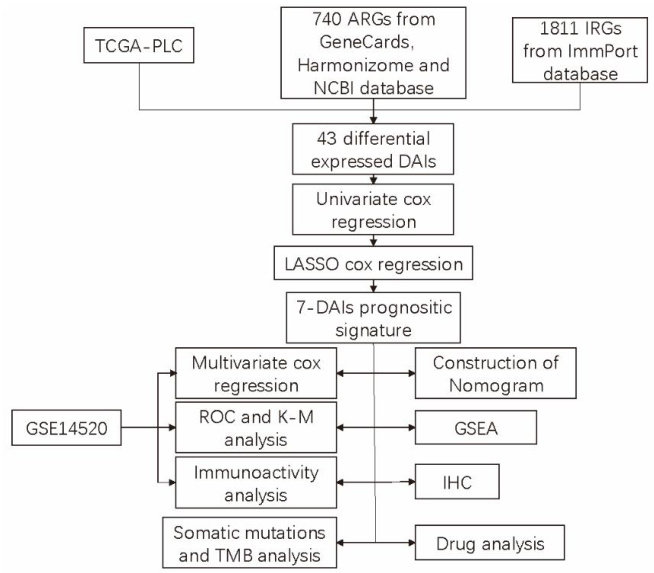
Abstract: Objective Toestablisha prognostic modelfor primary liver cancer (PLC)using bioinformatics methods.Methods Basedon the data from 404 patients in the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA)database,we constructed a prognostic model integratingthedierentiallyexpressedgenes,anoikisandimmune-relatedgenes (DAs)usinguivariateCoxregreioand theLASSO-Cox approach.Thepredictiveabilityof the model was evaluatedusing Kaplan-Meiermethodand receiveroperating characteristiccurves,andanomogramwasdevelopedtofacilitateitsclinicalaplications.Genesetenrichment analysis (GSEA)wasperformedtoexploretheassociatedpathwaysandrelationshipbetweentheDAIsandthetumor immune microenvironment,and the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of liver cancer drugs was calculated using the "pRRophetic"Rpackage.WealsodetectedtheexpressionofSEMA7Ainpairedtumorandadjacenttissesfromlivercancer patients.Results Weconstructedandvalidatedaprognosticmodelbasedon7AIs(NR4A3,EMA7A,IL11AR,C5,GF andSPP1),andobainedconsistentresultsinboththeTCGAtrainingcohortandGEOvalidationcohort (GSE14520),wrethe patients in the low-risk group were characterized by more favorable clinical outcomes and immune status.Byintegrating this prognostic signature withclinicalinformation,acompositenomogram was generated.Somatic mutationanalysisshowed that TTN,TP53,andC1mutaionsaccountedforthelargestproportionoftotalmutationsandtepatientsitelow-isklow-TMBgrouphadhighersurvivalrate.Drug sensitivityanalysis revealed diferences insensitivitytochemotherapeutic agents between high-and low-riskgroupsandbetweenTP53 mutationsand non-mutations.Inclinicaltissue specimens, SEMA7Aexpressionwassignificantlyhigher inlivercancertissesthanintheadjacenttisses.Concusions Weestablisheda newprognosticmodelbasedonDAIsforpredictingclinicaloutcomesandtherapeuticresponseofpatients withprimaryliver cancer.
Keywords: liver cancer;anoikis;immune-related genes; prognosismodel; bioinformatics
原发性肝癌(PLC)是全球常见的消化系统恶性肿瘤,其发病率和死亡率居高不下。(剩余16352字)