金樱子通过调控Src-AKT1轴抑制肺动脉高压平滑肌增殖

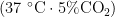
打开文本图片集
Abstract:ObjectiveToinvestigatethesynergisticmechanismof thetraditional ChinesemedicineRosalaevigataMichx (RLM)for treatmentof pulmonaryarterial hypertension (PAH).Methods Network pharmacologicalanalysis wascarriedout toscreentheactiveingredientsofRLMandPAHdiseasetargetsandconstructthe"component-target-disease"interaction network,followedbygeneenrichmentanalysisandmoleculardockingstudies.Ithecellexperiments,primaryculturesofat pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells were exposed to hypoxia for 24h and treated with solventor100,200 and 300mg/mL RLM,and thechanges incellproliferation were detectedusing Western bloting forPCNAand immunofluorescence staining. Intheanimal experiment,maleSDats wererandomizedinto5controlgroup,monocrotaline(MCT)solvent group,andMCT with RLM (100,200 and 300mg/mL )treatment groups. HE staining and immunofluorescence staining were used to observe histopathological changes in the pulmonary blood vesselsof therats.ResultsSevencoreactive ingredients (including β -sitosterol and kaempferol) in RLM and 39key disease targets were identified,and molecular docking showed that SRC wasa high-affinitytarget.KEGGenrichmentanalysisshowedthatthediferentialgenesweresignificantlyenrichedincalcium signaling andPI3K-AKTpathways.Inrat pulmonaryarterialsmooth muscle cels,hypoxicexposuresignificantlyup-regulated celularexpressonofPCNAandphosphorylationlevelsofSrcandAKT1,whichwereobviouslyloweredbyRLMtreatment. In RLM-treated rat models,the mean pulmonaryartery pressreand right ventricularhypertrophy index (Fulton index)were significantlyreduced,thetricuspidannularplanesystolicexcursion (TAPSE)wasimproved,andpulmonaryvascularwal thickeningand fibrosiswereobviouslyameliorated.ConclusionRLMinhibitspulmonaryarterial smooth musclecell proliferationinratmodelsof hypertensionpossiblybyregulating theSrc-AKTaxis,suggesting thepotentialofRLMasa new natural drug for treatment of pulmonary hypertension.
Keywords: pulmonary hypertension; smooth muscle cell proliferation; AKT1; Src; network pharmacolog
肺动脉高压(PAH)是一种危及生命的疾病,病情进展最终会导致右心衰竭和死亡[1]。(剩余25027字)