中国人群外周血MLPH基因高甲基化与冠心病相关

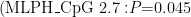
打开文本图片集
Abstract: ObjectiveToinvestigatetheassociationbetweenmethylationlevelsoftumorsuppressngsubtransferablecandidate1 (TSSC1)and melanophilin (MLPH) genes in peripheral blood and coronary heart disease (CHD)in Chinese population. MethodsThiscase-controlstudywasconductedin86CHDpatientsand95healthyindividuals,whosemethylationlevelsof TSSC1 and MLPH genes in peripheral blood were determined using mass spectrometry. Mann-Whitney U test was used to comparethe methylationlevels indiferentsubgroups.Thecorrelationof TsSC1and MLPHgene methylation levels withage andgender were evaluated using Spearman correlationcoeffcientand contingency coefficient,respectively.Results Comparedwiththehealthyindividuals,theCHDpatientsshowedasignificantcorrelationbetweenMLPHhypermethylation and myocardial infarction (MI) (MLPH_CpG_2.7: P=0.045; MLPH_CpG_3/cg06639874: P=0.049; MLPH_CpG_5: P=0019),and thiscorelationwasevenstrongerinindividualsbelow65yearsofage(MLPHCpG_2.7:P-0014;MLPH_CpG_4:P-0001)and inmale subjects (MLPH_CpG_2.7:P=0.004;MLPH_CpG_3/cg06639874: P=0.04).The methylation levelof TsSC1 gene in peripheral blood was notfound tocorrelate with CHDorits subtypes.Conclusion Our findings suggesta corelationof MLPH hypermethylation inperipheralblood withCHDandMI inChinese population,especiallyinindividuals below 65yearsand in male individuals.
Keywords: coronaryheartdisease; TssC1; MLPH; DNAmethylation; peripheral blood
冠心病(CHD)是全球死亡率最高的疾病之一[]根据《中国心血管健康与疾病报告2021摘要》,我国约有1139万CHD患者,给社会带来了巨大的经济负担[2]。(剩余13735字)