清肾颗粒通过调控miR-23b及Nrf2通路改善慢性肾脏病湿热证患者的肾功能:基于网络药理学和临床试验

打开文本图片集
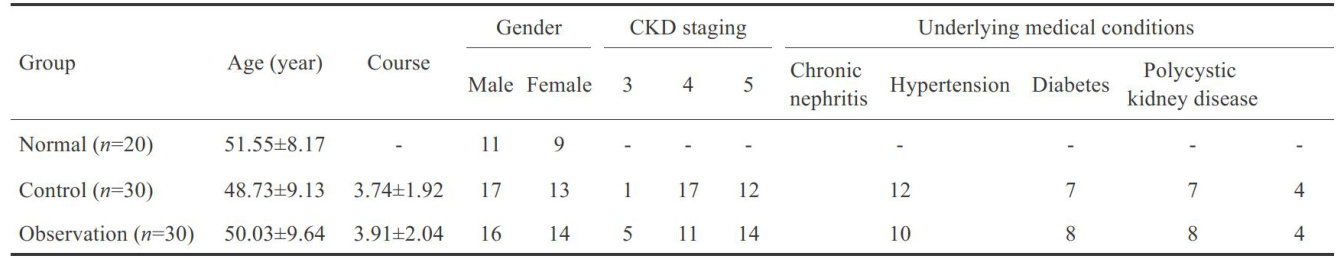
Abstract:ObjectiveToinvestigatethetherapeuticmechanismofQingshenGranules(QSG)inpatientswithchronickidney disease (CKD)damp-heat syndrome. Methods The regulatory targets of QSG were retrieved and mapped using TCMSP and UniProt.SmallRNA sequencing technology was used to screen the target genes ofchronicrenal failure damp-heat syndrome toconstruct the "active ingredients-intersectiontargets-diseases"network,folowedby KEGG pathwayenrichment analysis and molecular docking of thecore targets.Sixtypatients with CKD (stage3-5)presenting with damp-heatsyndrome and not undergoing dialysis were randomized equally into two groups for conventional Western medicine treatment (control group) and additionaltreatmentwith QSG (observation group)for8 weeks,with20healthyindividualsasthe normalcontrol group. The expresionlevelsof miR-23b-5p,Nrf2andHO-1proteininperipheral bloodmononuclearcels (PBMC),renalfunction indicators (Scrand eGFR),andserumROS,AOPPand PON-1 levels were compared among the3 groups after the treatments. ResultsSixiedteirgted, PPARG,PIK3CA,APP,PIK3R1,andBECN1. MiR-23b-5pexpression wassignificantlyup-regulatedin CKDamp-heat syndrome,in which theNrf2 pathwayabnormality playedanimportant pathogenicrole.Molecular docking results suggested goodbindingactivityofthecore targets withtheactive ingredientsof QSG,and NFE2L2 hadthestrongestbinding with luteolin. In patients with CKDdamp-heatsyndrome, QSG treatmentsignificantlydecreasedserum Scr, ROSand AOPPlevels, obviouslyimproedeGFRandincreasedserumON-1levelsexpressionevelsofNrf2andHO-1proteinsinsdthe expresion level of miR-23b-5p.Conclusion QSG can improve therenal function in patients with CKDdamp-heat syndrome posiblybyupglag-bpesonaigtfiodttaydcgtiels. Keywords: Qingshen Granules; chronic kidney disease; microRNA; Nrf2 pathway; network pharmacology
慢性肾脏病(CKD)是一种以高发病率、不良预后以及高昂医疗成本为特征的全球性重大健康问题。(剩余16216字)