具有光热抗菌活性的聚多巴胺修饰藻蓝蛋白纳米颗粒促进小鼠伤口皮肤愈合

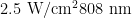
打开文本图片集
Abstract:ObjectiveToevaluatethephotothermalandantibacterialactivitiesofpolydopamine-modifiedphycocyanin nanoparticles (PDA@PCNPs)andtheircapacity forpromoting wound healing.Methods PDA@PCNPs weresynthesized from phycocyanin (C-PC)and dopamine hydrochloride using aone-pot method.The photothermalactivityof thenanoparticles was assessed in vitro by 808nm laser irradiation,their biocompatibility was evaluatedusing CCK-8assay,and their photothermal antibacterialactivitybyplatecolonycounting.InadultmaleBALB/mice,twosymmetricalful-ticknesskinwounds (1.0cm ×1.0cm )werecreatedonboth sidesofthespine,and 200μL ofStaphylococcusaureussuspension was inoculated into the wounds. The mice were divided into control group,A @ PCNPs group,and PDA@PC NPs with laser irradiation group,and wound healingratesand histomorphologicalchanges inthe woundtissues were evaluated ondays0,7and14aftermodeling. Results The synthesized PDA@PC NPs exhibited no obvious cytotoxicity up to a concentration of 500μg/mL and showed strongphotothermalandantibacterialactivitiesinresponseto 808nm laserirradiation.In themouse models, thesize ofthe infected skin wounds showed substantial reduction at7and14 daysin PDA@PCNPsgroup and PDA@PCNPs withlaser irradiationgroup,andthemeanwoundhealingratewasfasterinthelatergroup.HEstainingandMasson'strichrome stainingrevealedextensivegranulationtissueformationandcolagendepositiononthewoundsurfacesinbothof the treatment groups,and these changes were more obvious in the PDA@PCNPs with laser irradiation group. Conclusion PDA@PCNPs possessexcellentphotothermalandantibacterialactivitiesandcanefectivelypromote wound healinginmice.
Keywords: polydopamine; phycocyanin; photothermal therapy; wound healing
皮肤组织作为人体最大的器官,也是人体重要的物理屏障,在抵御微生物、调节代谢和维持内环境稳定等方面发挥着关键作用。(剩余14799字)