肿瘤微环境特异性CT影像组学标签预测非小细胞肺癌免疫治疗疗效

打开文本图片集
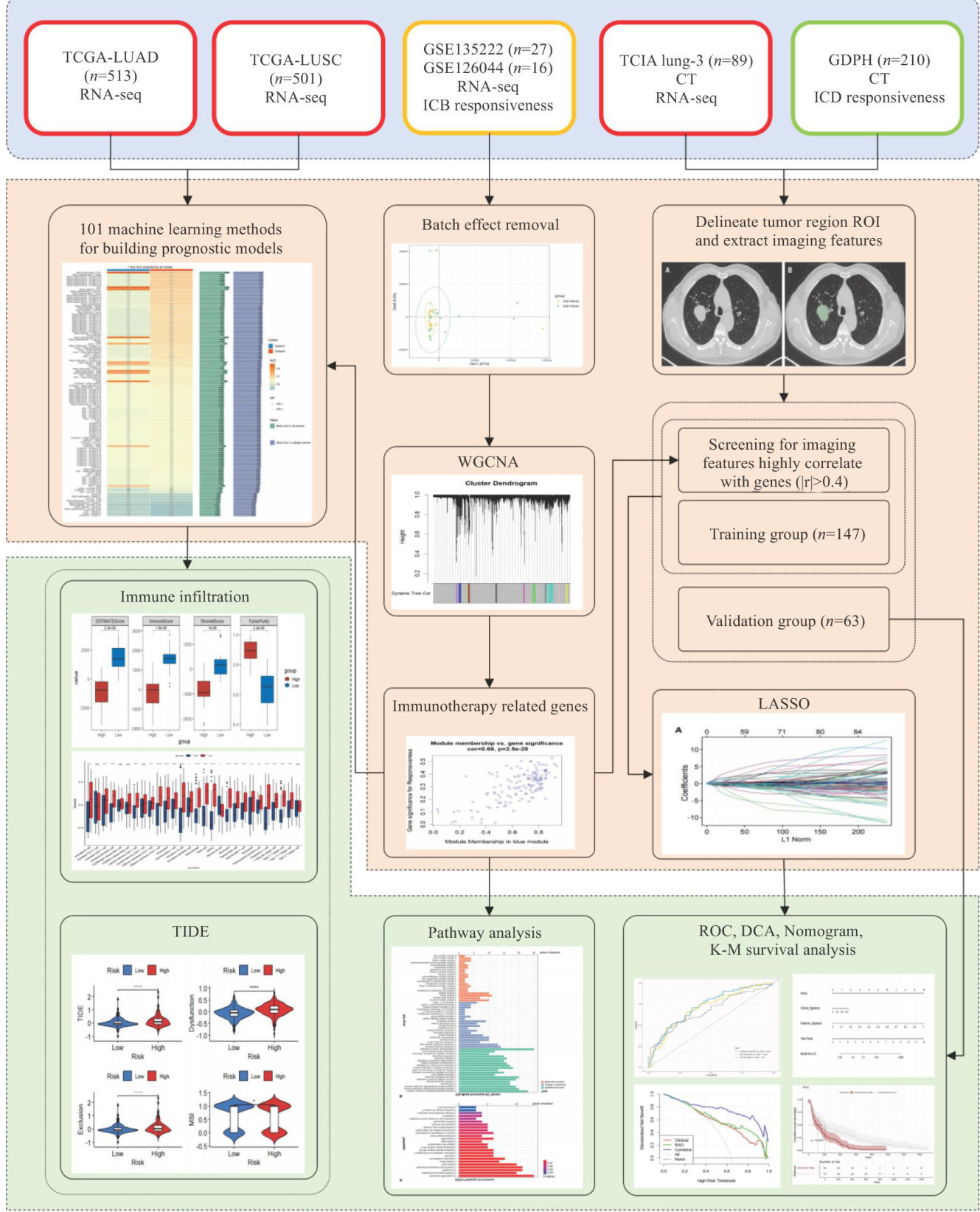
Abstract:ObjectiveToconstructanomogramforpredictingtheeficacyofimmunecheckpointinhibitors(ICIs)inadvanced non-small cellungcancer (aNSCLC)byintegratingchest CTradiomics signature thatreflects the tumormicroenvironment (TME)andclinical parametersofthepatients.MethodsTranscriptomicandCTimagingdatafromTCGA,GEOandTCIA databases were integrated for weighted geneco-expresionnetwork analysis (WGCNA)ofthe GEOcohort toidentify the immunotherapy-related genes (IRGs)asociated with ICIs response. A prognostic model was built using these IRGs in the TCGA cohort to assessimmune microenvironment featuresacrossdiferent risk groups.Radiomics features were extracted from TCIA lung_3 cohort using PyRadiomics,and 94 features showing strong association with IRGs ( |r|>0.4) were selected. A retrospectivecohortconsistingof210aNSCLCpatientsreceivingfirst-lineICIsatGuangdongProvincialPeople'sHospitalwas analyzedand divided into training (n=147)and validation (n=63) groups. Leastabsolute shrinkage and selection operator was usedforradiomicfeaturesselectionandlogisticegressionwasappliedtoonstructacombinediical-radiomicmodeland nomogram for predicting ICIs therapyresponse.Theperformanceof the model wasevaluatedusingROCcurve,calibration curve,and decision curve analysis.Results WGCNA identified84 IRGsenriched in immune activation pathways.The combined model outperformed individual models in both the training (AUC=0.725, 95% CI: 0.644-0.807) and validation cohorts (AUC=0.706, 95% CI:0.577-0.836).Calibration curveand decision curve analyses confirmed the clinical efcacy of the nomogram forpredicting ICIs therapy response inaNSCLC patients. Conclusion Thegenomic-radiomic-clinical multidimensionalpredictiveframework establishedinthisstudyprovidesaninterpretablebiomarkercombinationandclinical decision-making tool for evaluating ICIs eficacyin aNsCLC, potentiall facilitating personalized immunotherapydecisionmaking.
Keywords:non-smallcellungcancer;immunechckpoint inhibitors;tumor microenvironment; machinelearning;radiomics
肺癌在全球范围内发病率和病死率居高不下,其中非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)占肺癌病例的 85% ,晚期患者的总体生存预后较差1。(剩余18841字)