低氧环境下NLRP3信号通路促进非酒精性脂肪性肝炎小鼠的肝细胞焦亡

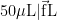
打开文本图片集
Abstract:ObjectiveToinvestigatetheregulatoryroleof theNLRP3signalingpathwayinhepatocytepyroptosisin nonalcoholicsteatohepatitis (NASH)underhypoxia.MethodsTwenty-fourmaleC57BL/6micewererandomizedequallyinto hypoxiccontrol(A)ypoxicNASHmodel(B),ypoxicNAH+NP3ihbitor(C)andhypoxicNAH+aspase-tor (D)groups.IngroupsB-D,the mice werefedamethioninecholine-deficient (MCD)dietunder hypoxicconditions (tosimulate a 5000m altitude)for6weeks;themice in groupsCandDreceived intraperitoneal injectionsof therespectiveinhibitors every otherday.Results Compared withthose in group A,the mice in groupBshowed significantly elevatedserum levelsof FBG, TC,TG,Adeadlrldntlorellidllageeoiod hepatic expressinsofNRP3,caspase-1,IL-1βandGDproteis,withbviousswelingcstaebreakagevacuozatio and outer membrane disruptionofthemitochondria,ribosome loss in the cytoplasm,destructionofthenuclear membrane, and pathologicalchangesoftheroughendoplasmic reticulum.TreatmentwithNLRP3inhibitorandcaspase-1inhibitorboth significantlyloweredseumevelsofTC,G,ALndAbutwithoutsigniicantlyectingG)intemousemodelsnd reducedliverldentmrcelliioollagpoiodeiolelsf GSDMDand IL-1β.Thetreatments also significantly improved pathological changes inthe mitochondria,ribosomes and endoplasmic reticulum in liver tissues ofthe mice. Conclusion NLRP3 signaling pathway plays a keyrole in promoting hepatocytepyroptosisinNASHmiceunderhypoxiccondition,andinhibitingthispathwaycaneffectivelyreduceliver inflammation, suggesting its potential asa therapeutic target for NASH treatment.
Keywords:hypoxia;nonalcoholicsteatohepatitis;hepatocytepyroptosis;NLRP3inflammatorypathway
非酒精性脂肪性肝病(NAFLD)是一种由于胰岛素抵抗、遗传易感性等因素引起的慢性肝脏损伤性疾病,可进展为非酒精性脂肪性肝炎(NASH)肝硬化甚至肝癌2。(剩余13212字)