大肠埃希菌QD68株对碳青霉烯类耐药的分子机制

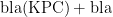
打开文本图片集
[中图分类号]R965 [文献标志码]A [文章编号] 2096-5532(2025)04-0609-04
doi:10.11712/jms.2096-5532.2025.61.131
[Abstract]ObjectiveTo investigatethe molecular mechanism of carbapenem resistance in Escherichiacoli strain QD68. MethodsTheVITEK2Compactsystemwasused toperforminitialidentificationandantimicrobialsusceptibilitytestingof strains,and Average Nucleotide Identity(ANI)wasusedforfinalidentificationof strains.NG-Test@CARBA 5asay was usedto detect carbapenemase.Ilumina MiSeq and Nanopore MinION sequencing platforms wereused toobtain the genomic sequecesof strains.Plasmidconjugationassyand S1nucleasedigestion pulsefieldgellectrophoresis wereused toanalye theplasmidsarried bythe strains.ResFinder4.1,PlasmidFinder2.0.1,andRASTwereusedforthebioinformaticsanalysis.ResultsThebioinfor matics analysis showed that E .coli strain QD68 carried one chromosome and four plasmids,which were named QD68-chr,pQD68- 1,PQD68-2,pQD68-NDM,and pQD68-IPM,respectively.This strain alsocariedtheblaNM-5andblaMP-8genes,whichwerelo cated on thepQD68-NDMplasmidand pQD68-IPM plasmid,respectively.Inadition,E.coli strain QD68couldtransferthe bla IMp-8gene to E.coli J53AziR through plasmid conjugation. ConclusionThe molecular mechanism underlying carbapenem resistance in E.coli strain QD68 may be attributed to the co-harboring of and blaIMP-8 genes. Therefore,it is necessary to monitor carbapenem-resistant Escherichia coli.
[Key words]Escherichia;carbapenemase;drug resistance,bacterial; bla NDM-5 ;bla IMP-8
抗菌药物耐药性给临床和公共卫生带来了重大挑战[1]。(剩余6632字)