菌藻共生下的水产养殖尾水“零排放”分析

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:X714 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1004—6755(2025)11-0060—03
Analysis of “zero discharge” in aquaculture tail water under symbiosis of bacteria and algae
SHEN Yubin
(RuralWork Office ofHengji Town,Jianhu County,Yancheng224763,China)
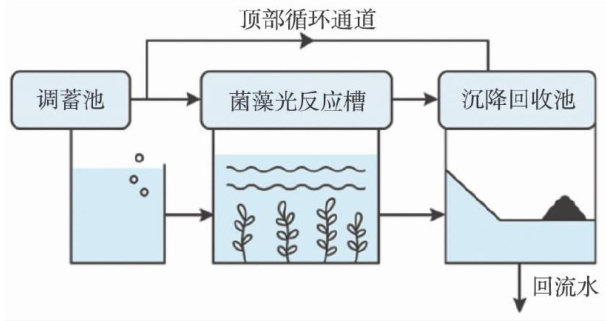
Abstract:To explore an eco-friendly approach for tail water treatment,this study investigates the construction model and operational strategies for a "zero discharge" system for aquaculture tail water based on the mechanism of bacterial一algal symbiosis. By analyzing the metabolic complementary mechanisms between bacterial communities and microalgae,a multi一module synergistic process centered around a photoreactor is proposed to establish a closed-loop system for the synergistic conversion of carbon,nitrogen and phosphorus. Using the aquaculture park in Sihong,Jiangsu Province as a case study,system deployment and operational efficiency were evaluated. The results demonstrate that the system achieves effective pollution reduction and synergistic resource recovery,confirming its feasibility and promotion for broader application in aquaculture tail water treatment.
Key words:bacteria一algal symbiosis; aquaculture tail water; zero discharge; synergistic nitrogen and phosphorus removal
近年来,水产养殖业的快速发展,导致尾水排放总量持续上升,其中氮、磷等营养盐负荷过高,已成为制约养殖业绿色转型的瓶颈。(剩余3685字)