萝卜种质资源抗根肿病鉴定及QTL-seq定位

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S631.1 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1673-2871(2025)08-037-08
Identification of clubroot resistance in radish germplasm resources and QTL-seq mapping
DANG Zengqing, QIAO Huifang (KaifengProductQualityInspectionandTestingCenter,Kaifeng475o4,Henan,China)
Abstract:Clubrootdisease,causedbyPlasmodiophorabraicaeWoronin,isagloballydistributedsoil-boredisease thatseriouslythreatens thesustainabledevelopmentof the Brassicavegetable production.Toclarifytheresistance levels ofradish germplasmresources and identify resistance loci,this studysystematicall evaluated the clubroot resistanceof 40radishvarieties trough integrated fieldnatural infectionandseedling-stageartificialinoculation methods.Segregating populations constructed from resistant and susceptible parents were subjected to QTL-seq-based mapping analysis.The resultsdemonstrated thatonelocalvarietyandfour hybridsexhibitedimmunity(I),onelocalvarietyand thre hybrids showed high resistance(HR),and threelocal varietiesshowed disease resistance(R).QTL-seq analysis identified fouresistance-associatedQTLsonchromosomes1,2,and5,withthemajor-effectlocusrs2.1locatedonchromosome2.This research sucessullyscreens multiple elite resistance sources and maps clubroot resistance loci inradish,providing crucial scientific foundations for disease-resistant breeding and gene cloning.
Key Words: Radish; Clubroot disease; Identification; QTL-seq mapping; Disease-resistant breeding
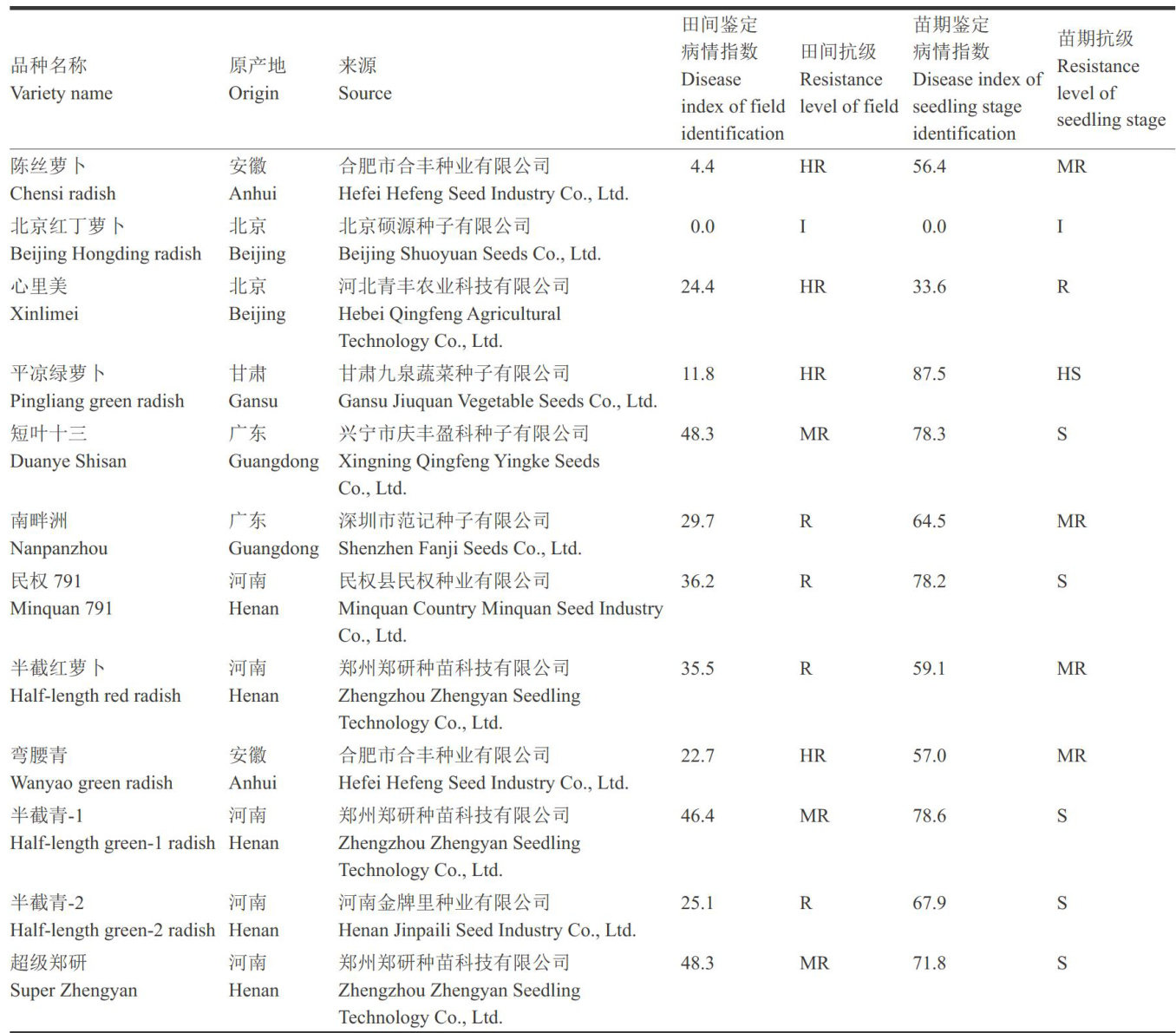
萝卜(RaphanussativusL.)是我国重要的十字花科根菜类蔬菜,具有较高的营养价值和经济价值,常年种植面积约120万 hm2[1-2] 。(剩余9449字)