基于网络药理学与表面等离子体共振的方法探讨巴戟天根治疗骨质疏松症的作用机制

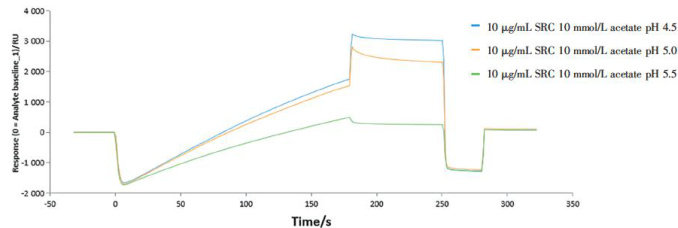
打开文本图片集
[中图分类号]R580 [文献标志码]A [文章编号] 1674-7887(2025)05-0448-08
Exploring theactionmechanismof Morinda officinalis Radix in treating osteoporosis based on network pharmacology and surface plasmon resonance*
LILiangl**,YANGWeihang²,XUJiahao1,XIAShuangl,JIHongjian³,SHIFengchaol*** (Department of Orthopedics,the SixthAfilatedHospitalofantongUniversityYanchenghirdPeople'sHospital,iangsu224Ool;Orthopediceatet Center,Tongling Municipal People'sHospital; School of Pharmacy,Jiangsu Medical College)
[Abstract]Objectie:Basedonthenetwork pharmacologyandsurface plasmonresonance technology,theactiveingredients andtargetsofMorindaoficinalisRadix(MOR)inthetreatmentofosteoporosis(OP)wereexplored.Methods:TobetterunderstandthemechanismsandtargetsofMOR,anintegratedanalyticalplatformwasbuiltbasedonnetworkpharmacologyncluding targetprediction,protein-proteininteractionnetwork,topologyanalysis,geneenrichmentanalysis,moleculardockingand surfaceplasmonresonance.Results:Usingthisplatform,weidentifiedkeychemicalconstituents inMOR,suchasathraquinone compounds,eta-sitosterol,dibutylphthalate,andoleicacid,thatexhibitanti-OPactivity.Theprotein-proteininteraction network showsthat thecorechemical components exertanti-OP efects through theestrogen signaling pathway,endocrine resistance,andfocal adhesion signaling pathway byacting oncertain targets.Theresults of molecular docking and surface plasmonresonanceindicatethatthereisagoodafinitybetweenthecorechemicalcomponentsandthekeytargets.Conclusion:thecorecomponentsofMOR,namelyanthraquinone-typecompounds,mayexertanti-OPefectsbymodulatingessetial target proteinssuchas SRC,EGFR,JUN,and BCL2 through various signaling pathways,including the estrogensignaling pathway,endocrine resistance,and focal adhesion.
[Keywords]osteoporosis;MorindaoficinalisRadix;networkpharmacology;moleculardocking;sufaceplasmonresonance; signaling pathway
骨质疏松症(osteoporosis,OP)是一种与性别和年龄相关的疾病。(剩余14194字)