黄精属植物叶绿体基因组系统发育与密码子使用偏好分析

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S567 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1000-4440(2025)09-1704-10
Abstract:To investigate the chloroplast genome phylogeny,codon usage bias paterns and related influencing factors of plants in the genus Polygonatum,the MISA,IRscope,and mVISTA were used to analyze chloroplast genome characteristics of eightplants inthe genus Polygonatum.CodonW1.4.2,CUSP,Excel,and MEGA11 wereutilizedtoperform codon biasand phylogenetic analysis.Theresults indicated that mononucleotiderepeatsequences composed of bases Aand Twerefrequentlyutilized.Theboundaries of thechloroplast genomes were highlyconserved,exhibiting minimalvariationin genomiccomposition.TheGCcontent incodons progresivelydeclinedfromthefirsttothethirdcodonposition,withapronouncedbiastowardbaseAorUat thethird position.Codonusagebiasinchloroplast genomes was shapedbymultiple factors,withnaturalselectionservingastheprimarydrivingforce.Utimately,ineidenticaloptimalcodonswereidetifiedas commontoalleightstudiedPolygonatumspecies.PhylogeneticanalysisrevealedthatPolygonatum hookeriandPolygonatumfrancheti exhibitedadistantrelationship totheothersixstudiedPolygonatumspecies.This studyprovidescrucialsupportforphylogeneticanalyseswithinthePolygonatumgenus,whilealsolayingatheoreticalfoundationfortheauthentication of Polygonatum medicinal materials,cultivar improvement,and genetic breeding efforts.
Key words:Polygonatum;chloroplast genome;codon bias;phylogenetic analysis
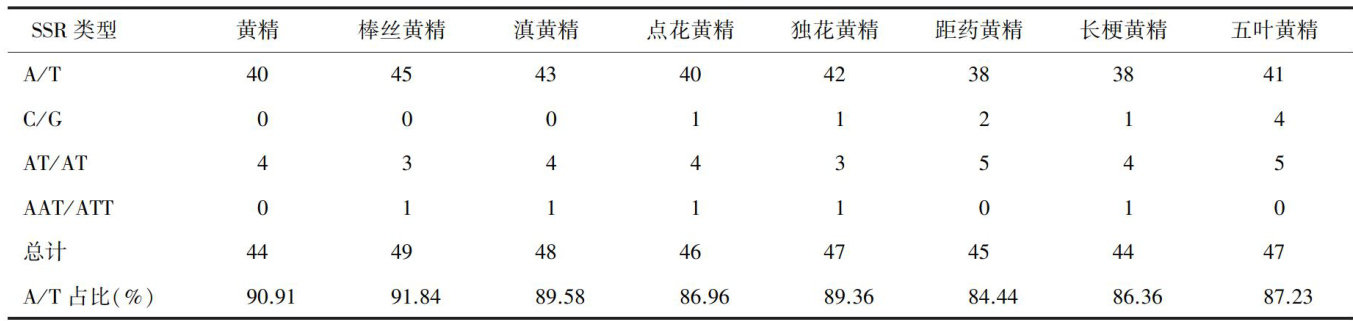
传统药材黄精素有“仙人余粮”和“百岁草”的美誉。(剩余12628字)