基于ENVI-met热舒适度模拟的热带传统院落空间选型研究

打开文本图片集
Research on Spatial Configuration of Tropical Traditional Courtyards Using ENVl-met Thermal Comfort Simulation
*
FU Yingtao,YANG Dinghai*,YUAN Yizhe
基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目“三生空间视角下海南岛传统村落文化地理特征及形成机理研究”(编号:52168002);海南省自然科学
基金项目“景观基因视角下海南岛传统村落活态保护及有机更新研究”(编号:725MS067)
Abstract
Keywords
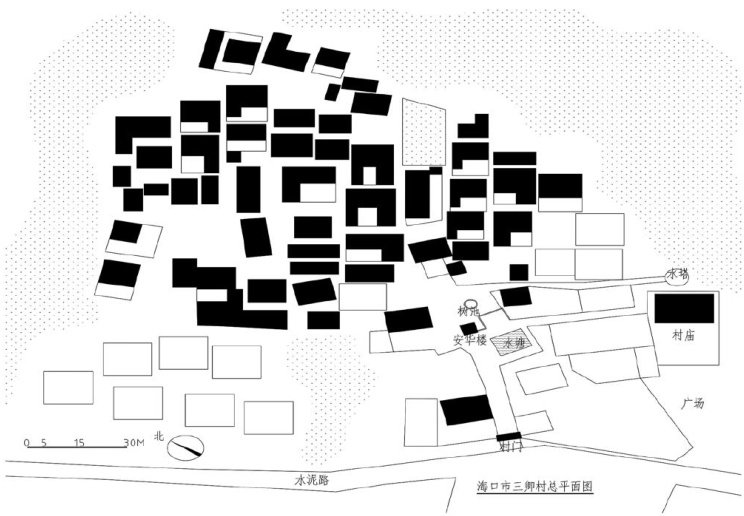
To identify the optimal spatial form of tropical traditional courtyards in hot-humid regions, thermal comfortwas employed as the key indicator for microclimate evaluation.Two typical courtyard types from Sanqing Village,a nationally recognized traditional ancient village in Haikou City,were selected for analysis. Using field surveys and ENVl-met numerical simulations,this study examined the relationship among courtyard depth,microclimate parameters,and thermal comfort to identify highly comfortable courtyard configurations. Results show that increasing courtyard depth significantly improves thermal comfort by lowering air temperature,increasing relative humidity,and enhancing wind speed,while decreasing depth produces opposite trends.Optimal thermal comfort was achieved at a courtyard depth of 8 meters,with linear courtyards outperforming L-shaped ones.Based on these findings,design strategies are recommended to optimize courtyard microclimates, including strategic vegetation placement and the use of perforated landscape walls to enhance ventilationand thermal performance.
Traditional courtyard; Spatial configuration;Microclimate; Thermal comfortlevel; ENVl-met simulation
文章亮点
1)采用ENVI-met数值模拟与实测相结合的方法,揭示了院落空间形态与热环境之间的内在作用机制;2)从类型学视角构建“院落空间形态-进深变化-微气候”的定量关系,为院落空间形态微气候参数化分析提供参考。(剩余13618字)