基于街景图像的桂林历史街区感知测度及空间分布特征研究

打开文本图片集
ZHAO Xinran,DENG Chunfeng*
基金项目:自然科学基金“桂北乡村发展类型与城乡融合发展模式研究”(编号:52268009)
Abstract
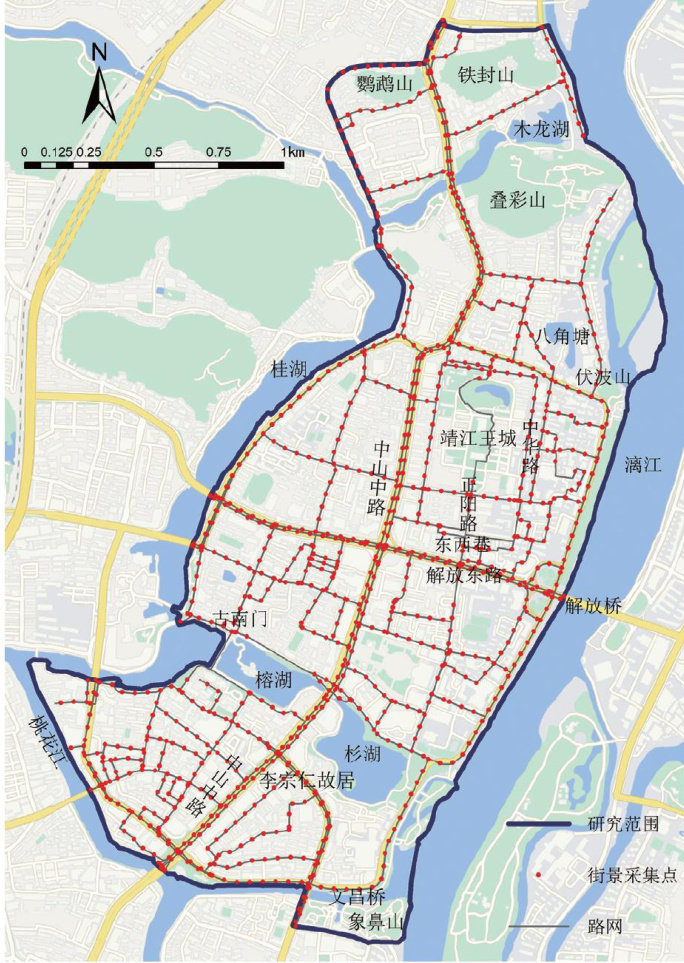
Historic street spaces not only serve material functions but also directly influence people's experiential and psychological perceptions.This study examines Guilin's historic streets, which face ageing infrastructure, declining landscape quality,and reduced vitality. A combined subjective-objective approach was adopted,employing street-view image segmentation and machine learning to quantify spatial quality and human perception. Partial Least Squares regression analysis was used to explore relationships between visual elements and perceptual responses. Results show that human perceptions exhibit spatial heterogeneity: beautyand richnessare focused within core scenicareas,liveliness is prominent along pedestrian streets and main roads,and boredom and oppression are common in older alleys.Spatial indicators display systematic patterns:green view index increases from the core to periphery,openness is higher at public nodesand main roads,enclosure is concentrated in traditional alleys,walkability is locally strong but generally weak,and motorization follows a 'high on main roads,low in blocks'pattern. Perception-space relationships are complex: green view,openness,enclosure,walkability, and motorization exert differing positive and negative effects on perceptions of beauty, liveliness,and oppression.Finally,based on the research findings,micro-renewal optimizationstrategies forGuilin'shistoricdistrictsare proposed.
Keywords
Historicdistricts;Streetview images; Semantic segmentation; Machine learning;PartialLeast Squares Regression;Microrenewal
文章亮点
1)引入街景图像语义分割与机器学习模型,构建主客观结合的历史街区感知测度框架,突破传统问卷与人工评价的局限。(剩余11627字)